Master's Thesis
TUMCREATE Ltd.
CHAIR OF INDUSTRIAL DESIGN TUM
2018, Summer Semester
Independent
Hard and Software:
HTC Vive, Unity


Accepted by the 5th International AR and VR Conference 2019
Question
How can we give our passenger a safer feeling while they are driven around in a car controlled 100% by a machine?
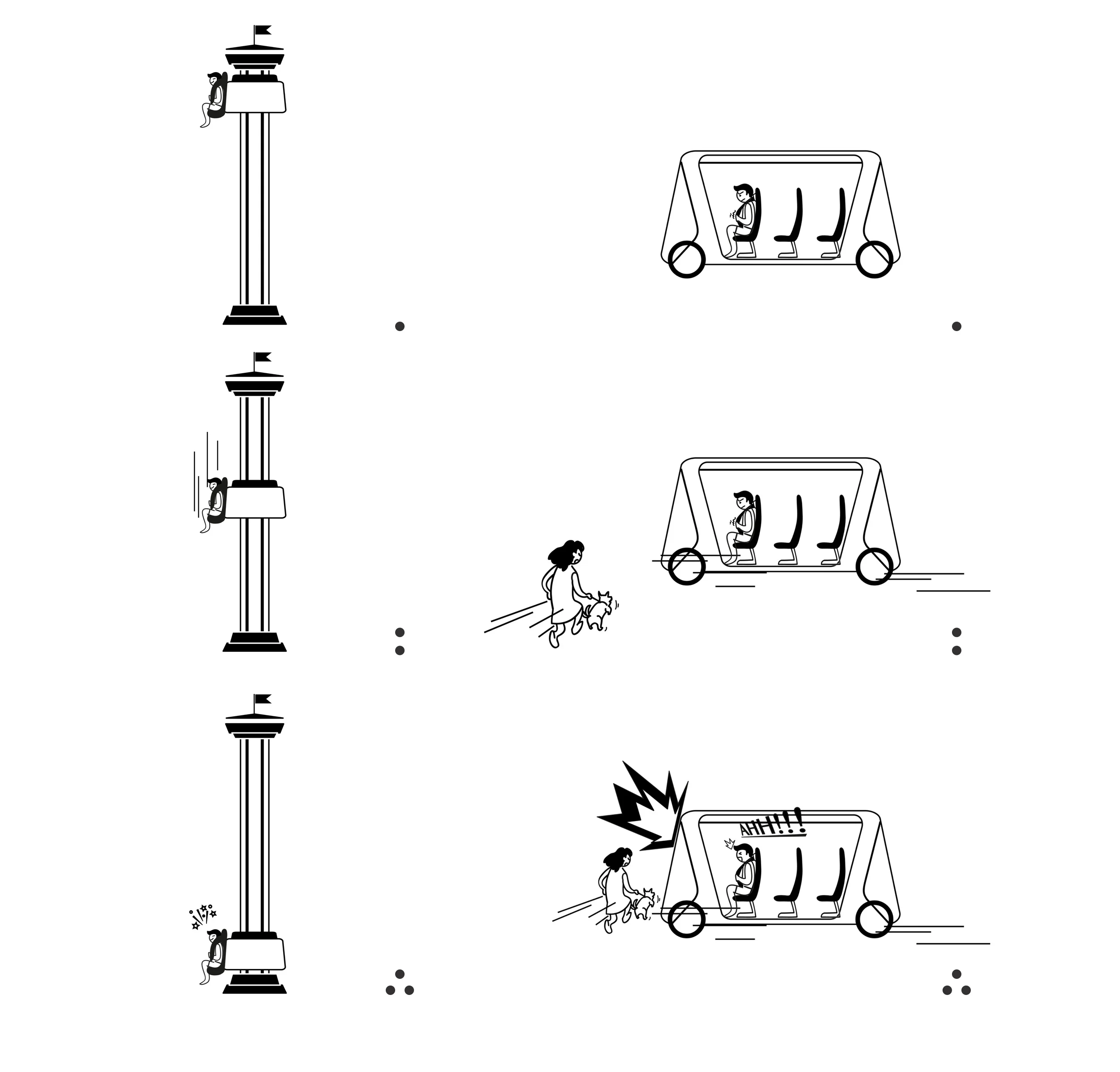
The consequence of losing control in an AV is no more fun.
Master’s
Thesis
Project
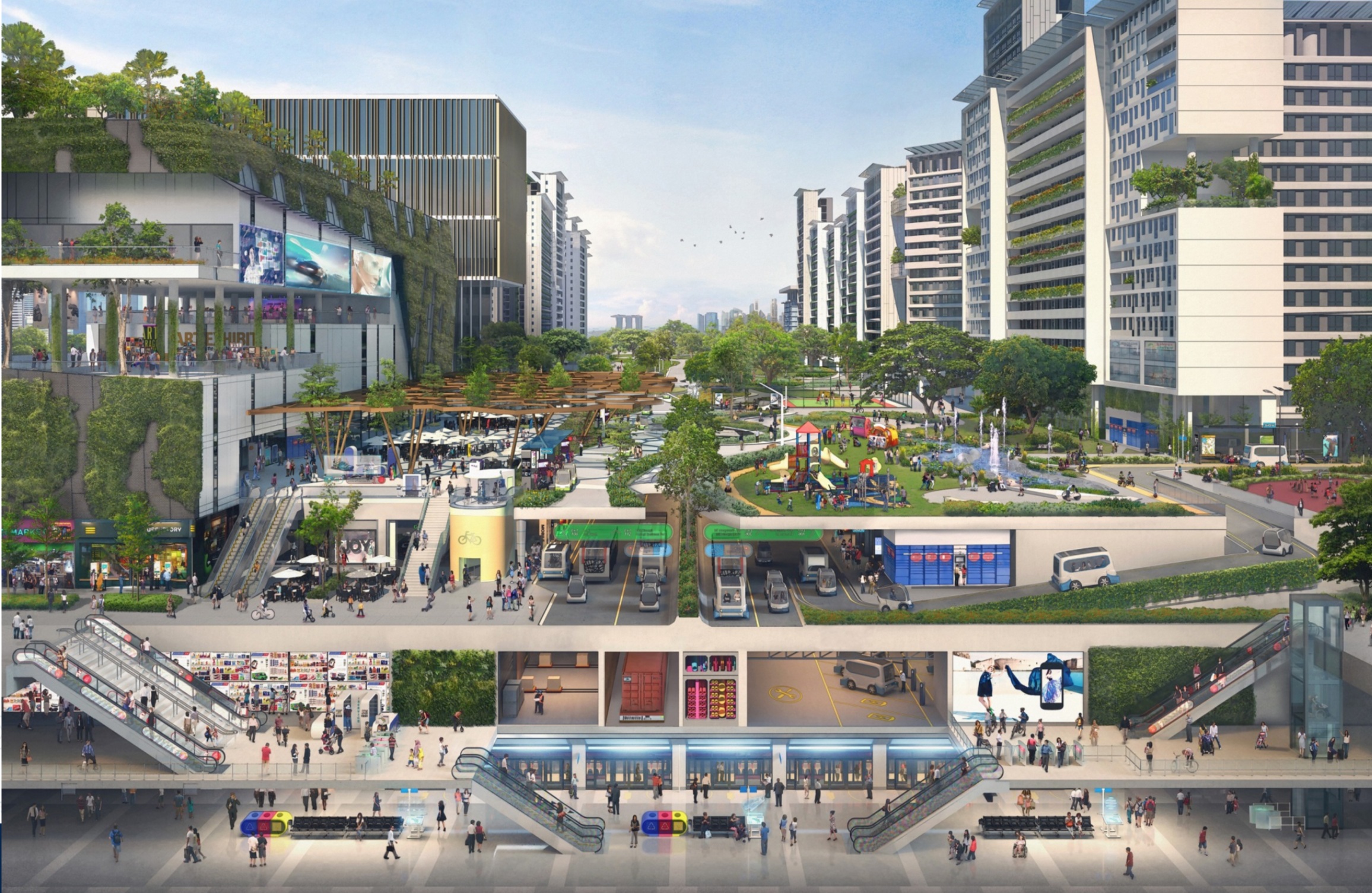
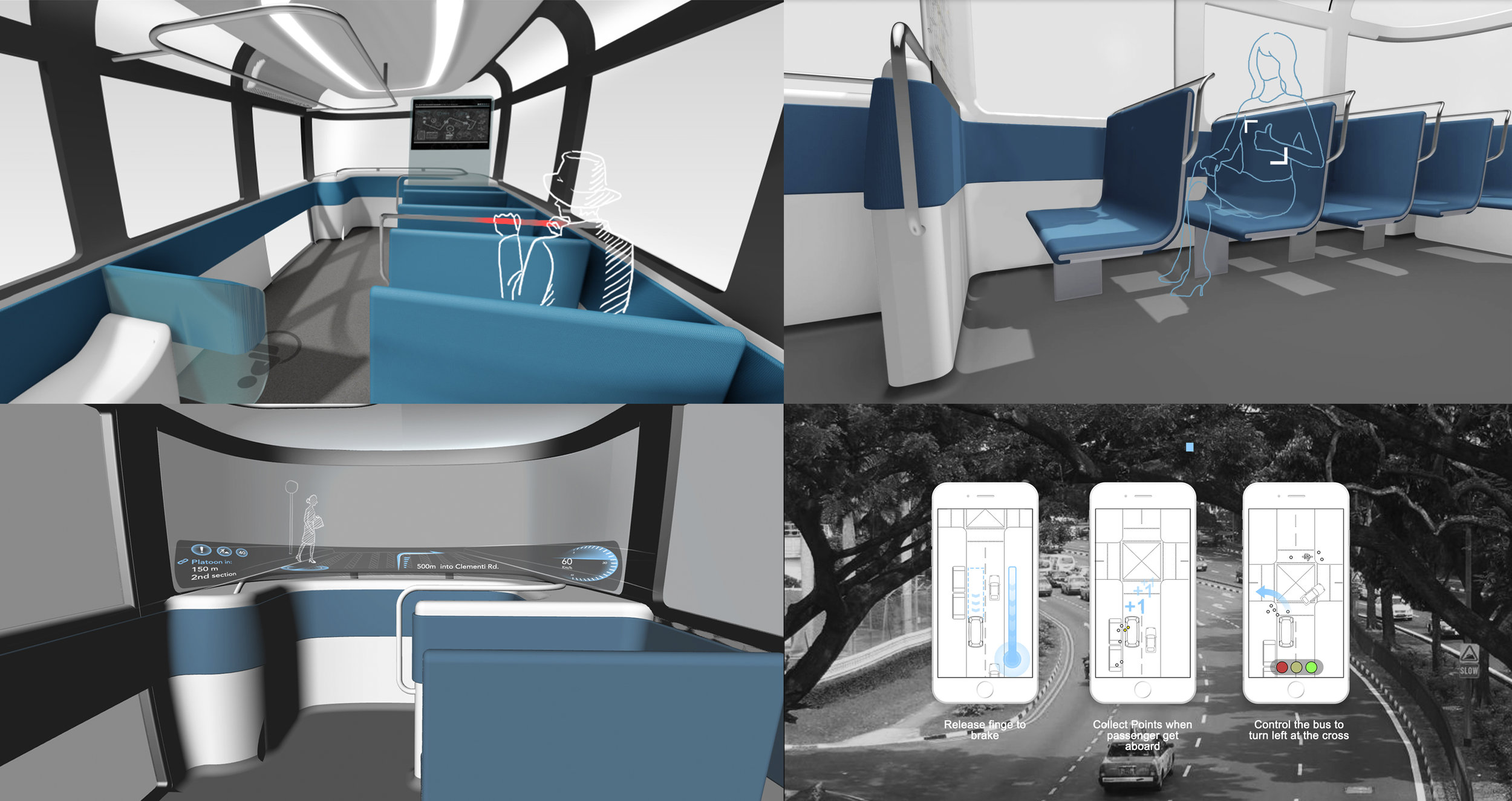
A HMI design for the fully autonomous bus
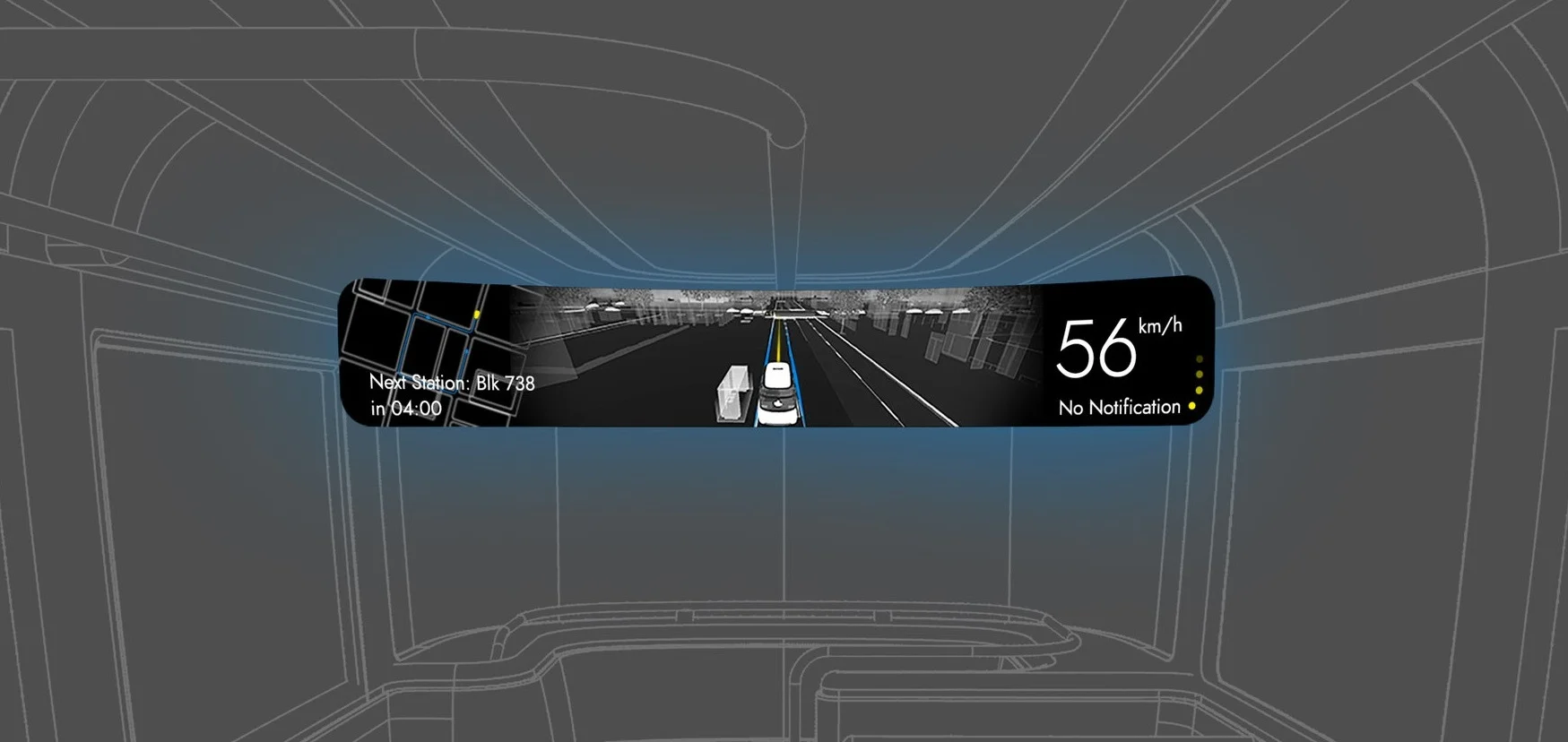
The project involves the potential sources of the anxiety feeling of the users that ride in an autonomous bus and potential design solutions. The purpose is to help the passengers reduce their anxiety while riding the autonomous vehicle (AV) and develop a positive attitude towards it. As a result, a HMI design has been developed as a solution-finding example in the framework of the UPTS project (Towards the Ultimate Public Transportation for Singapore) at the research institute TUMCREATE Ltd.
Main features
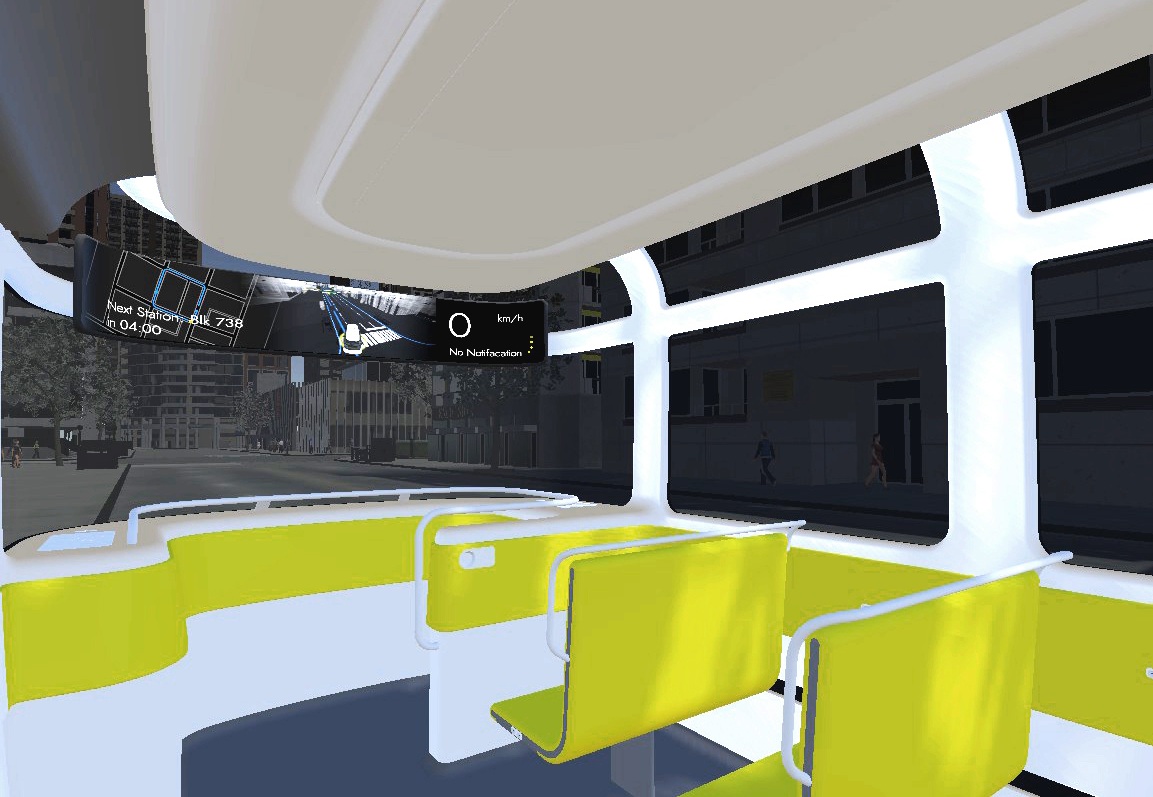
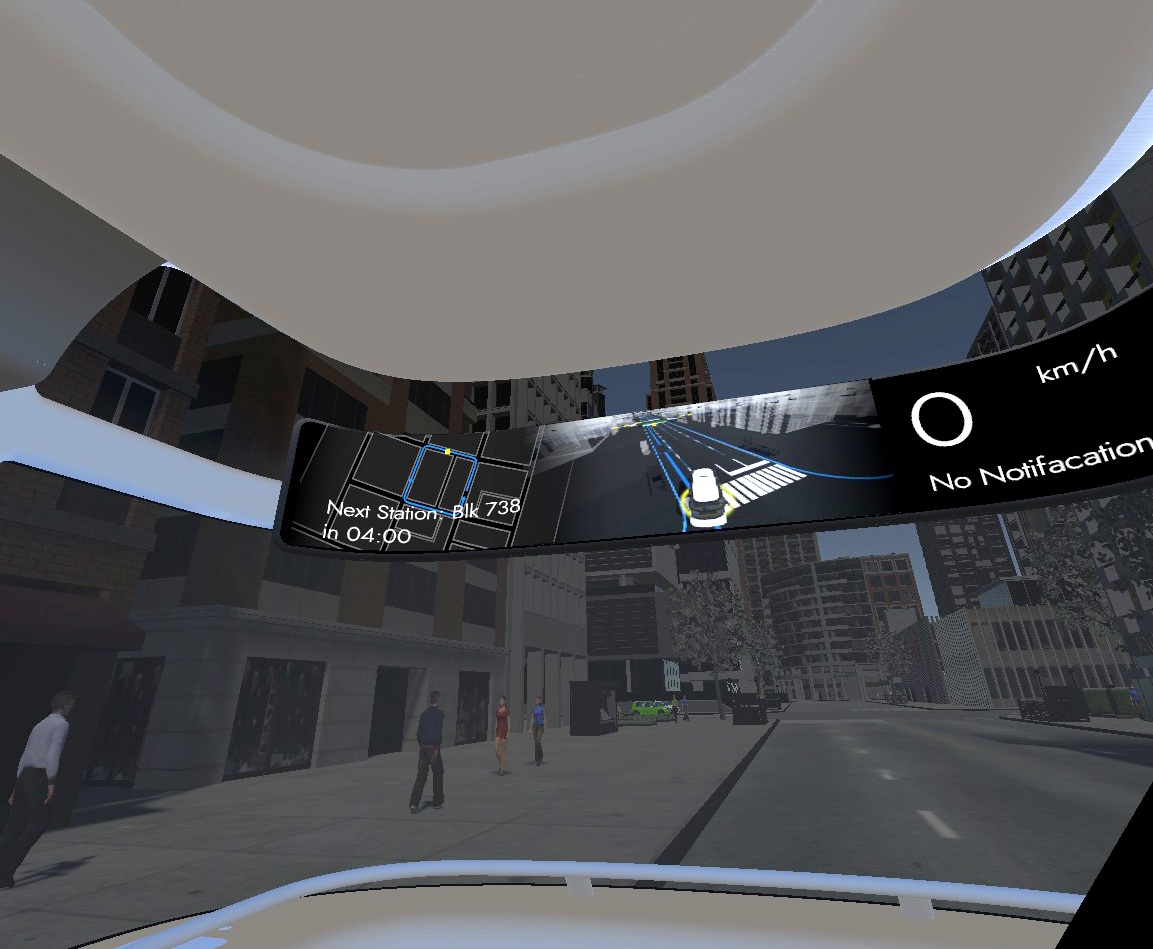
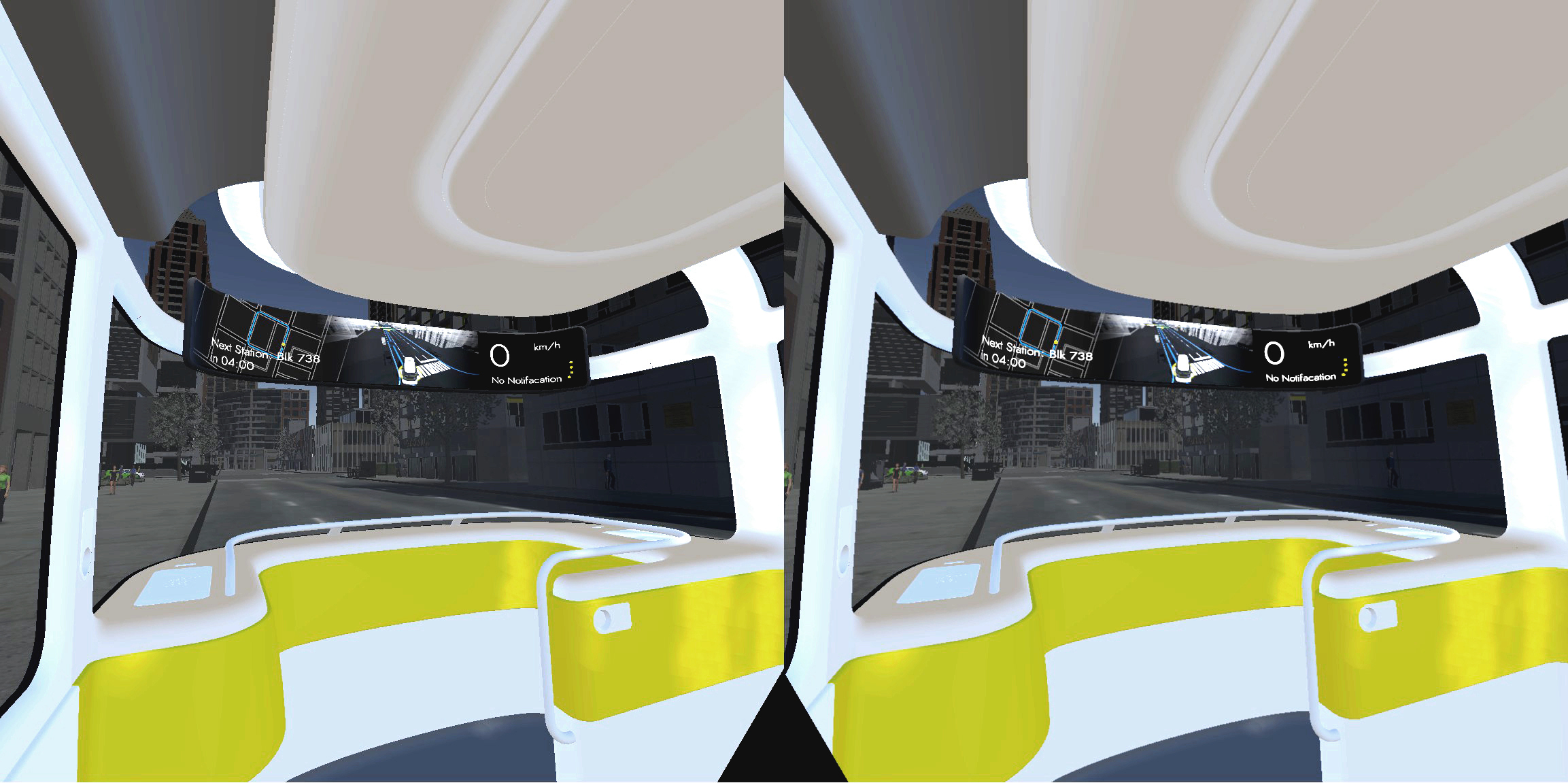
1. Transformed visual images in Real-time
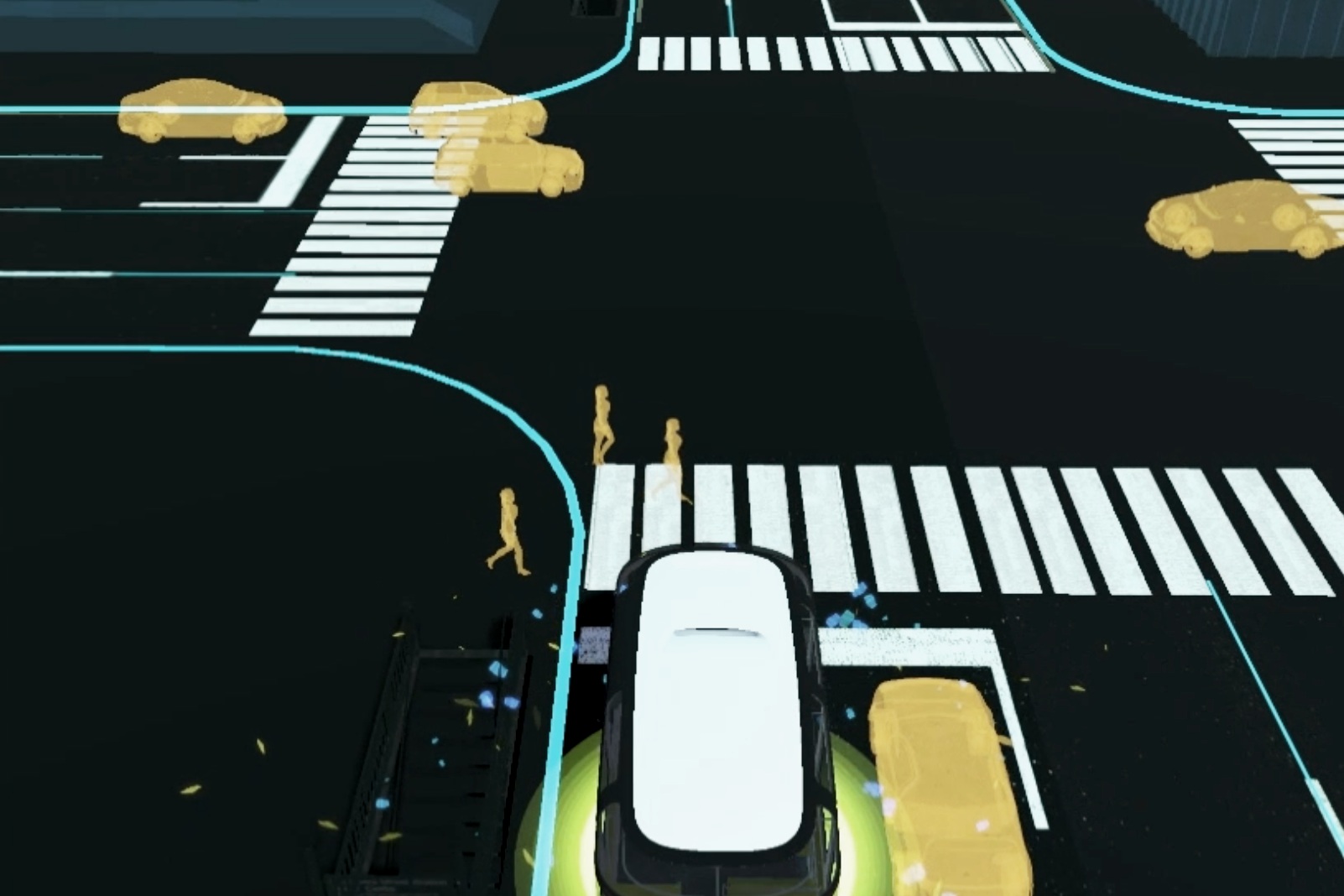
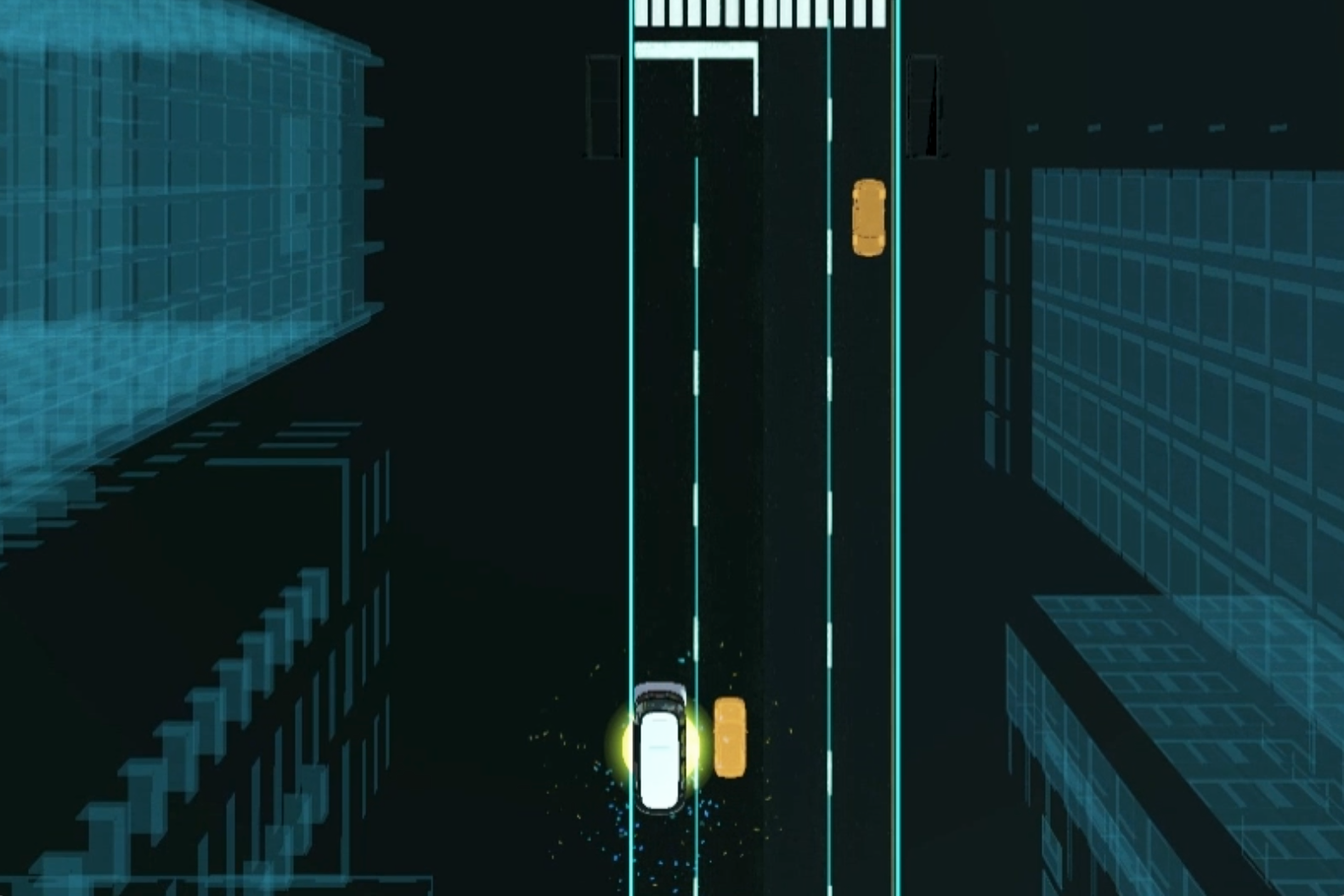
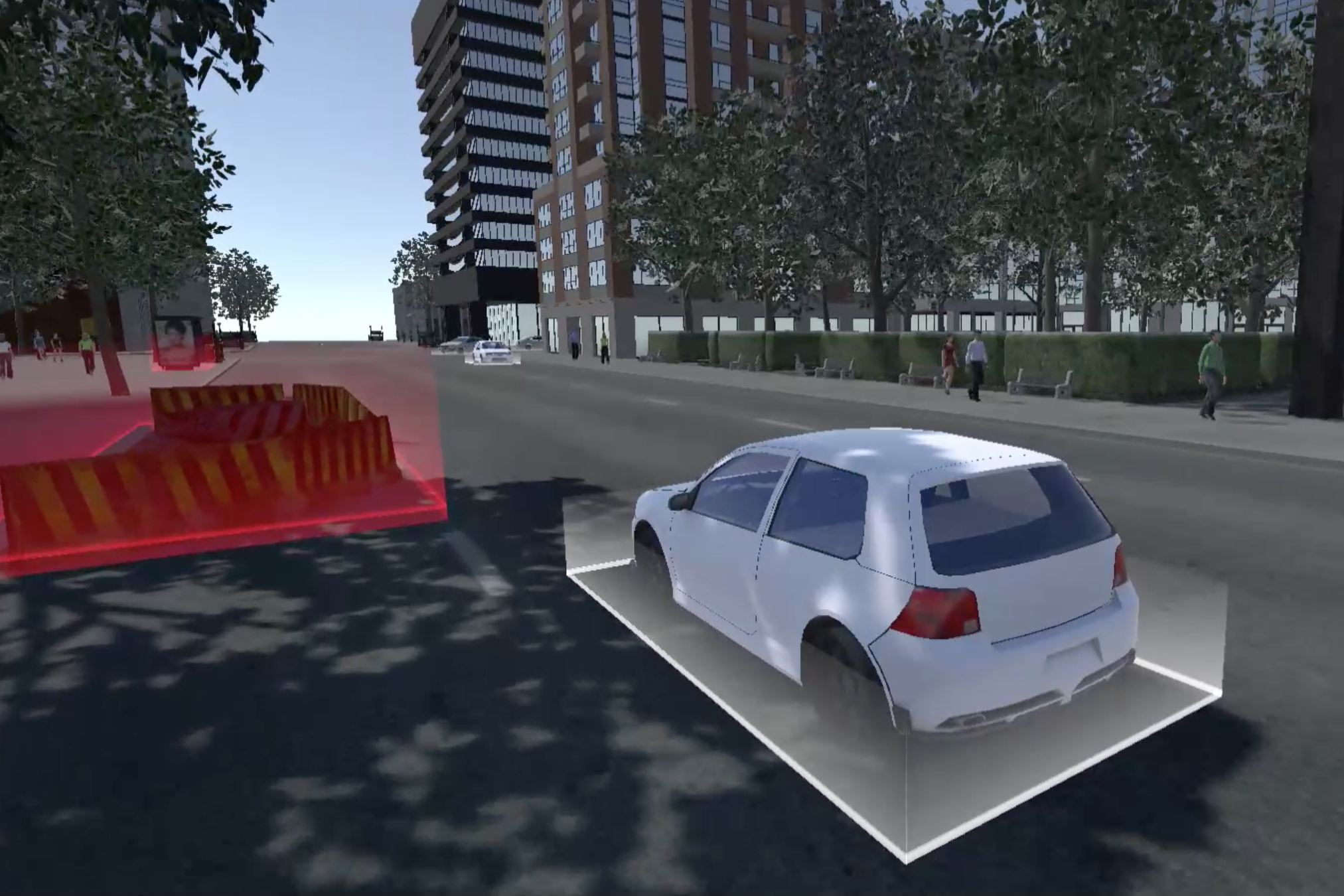
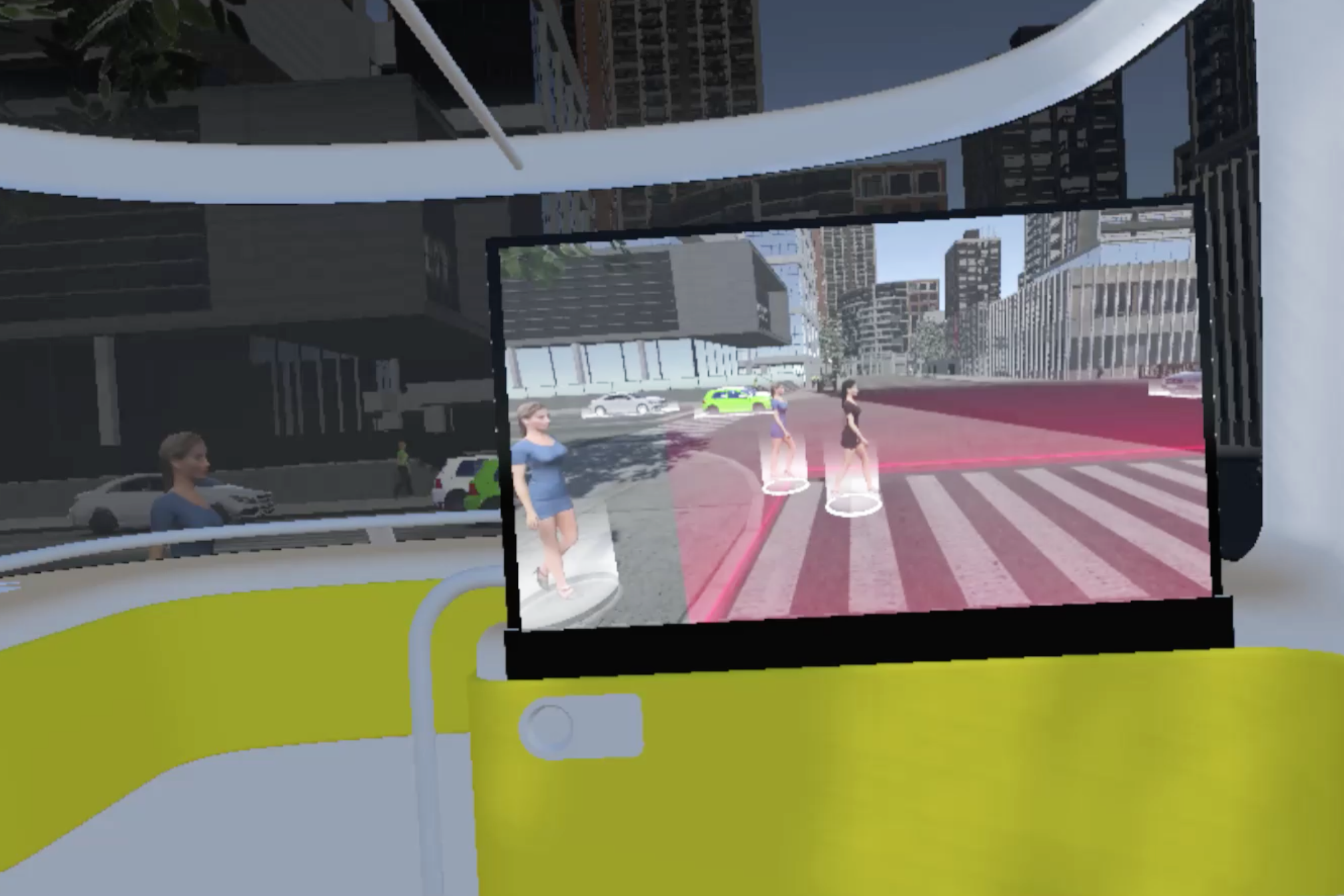
Showing the bus’s sensing status by using ripple effects (Ai. Ripple effects)
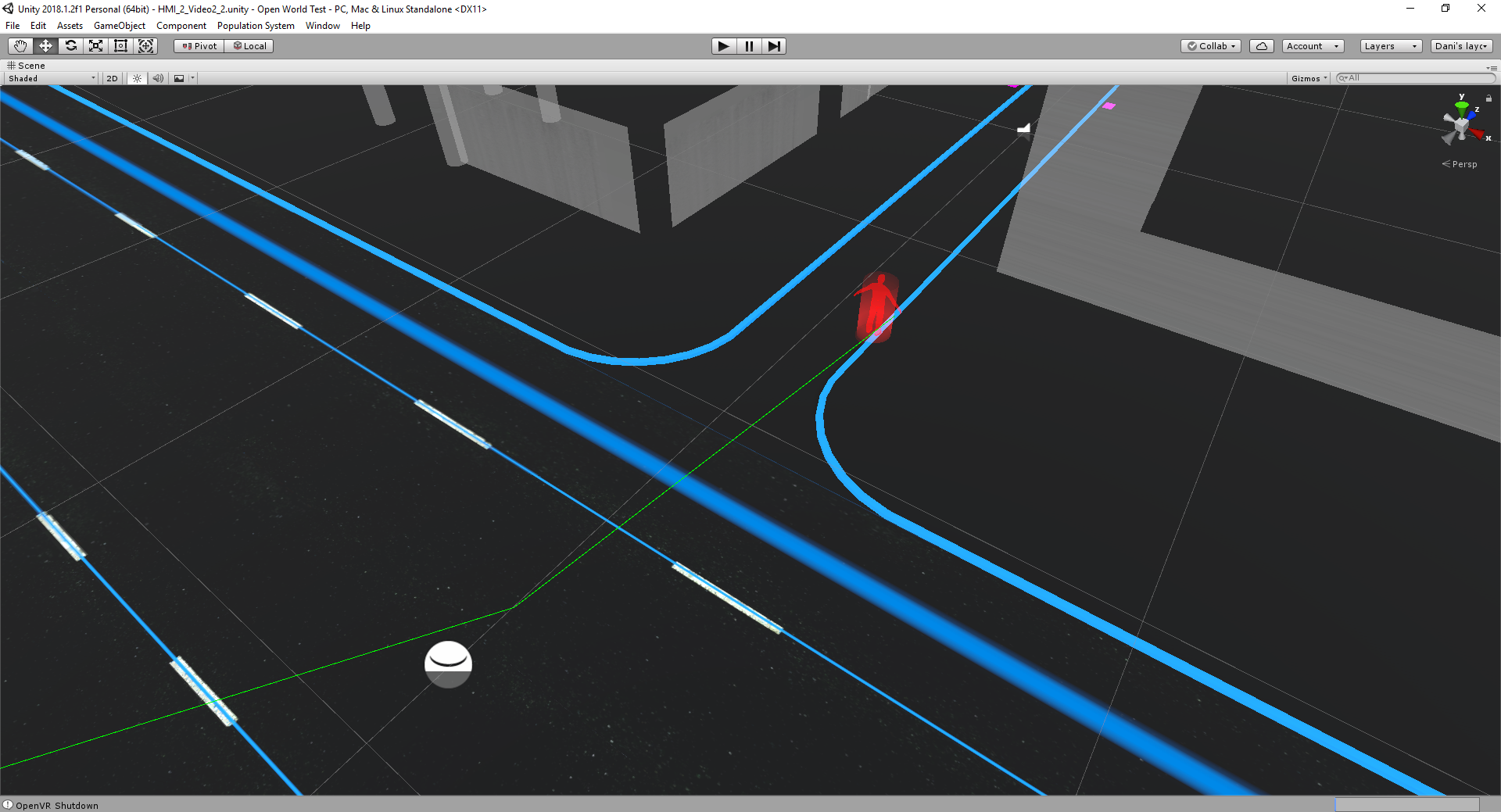
Representing its comprehensive detection of the environment (Ai. jaywalkers & traffic lights)
Indicating its intention by using a virtual railway (Ai. direction arrow)
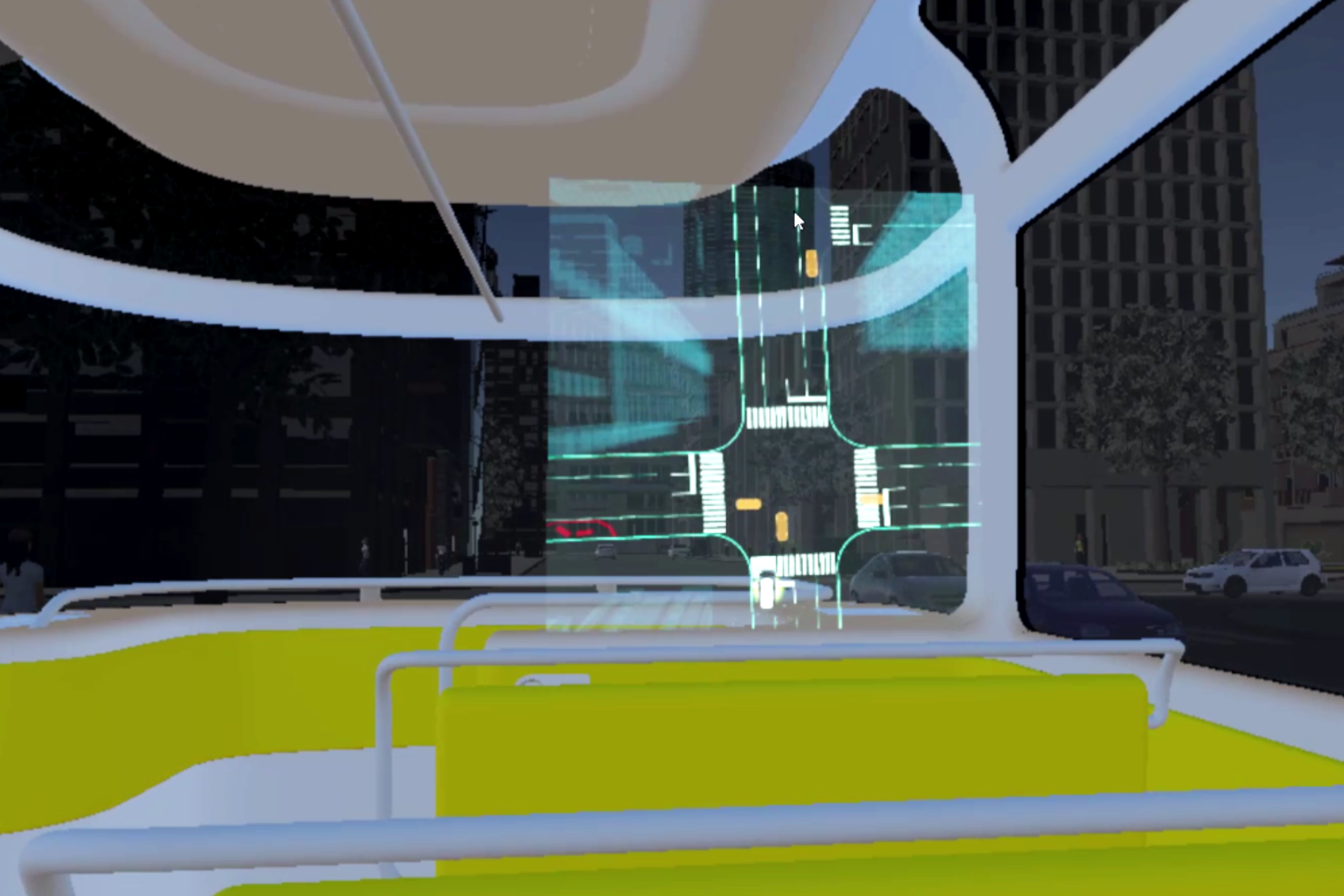
2. Holistic view of the route
According to the result of my user research, displaying the route overview can make passengers feel safer and being in control.
3. Connecting status and received notifications
The flickering points indicate the status of the connection to the holistic transport management system. Important messages that are received from it are shown, e.g. the bus needs to change its route because of an incident ahead.
Iterative
DOUBLE DIAMOND
DesigN Process
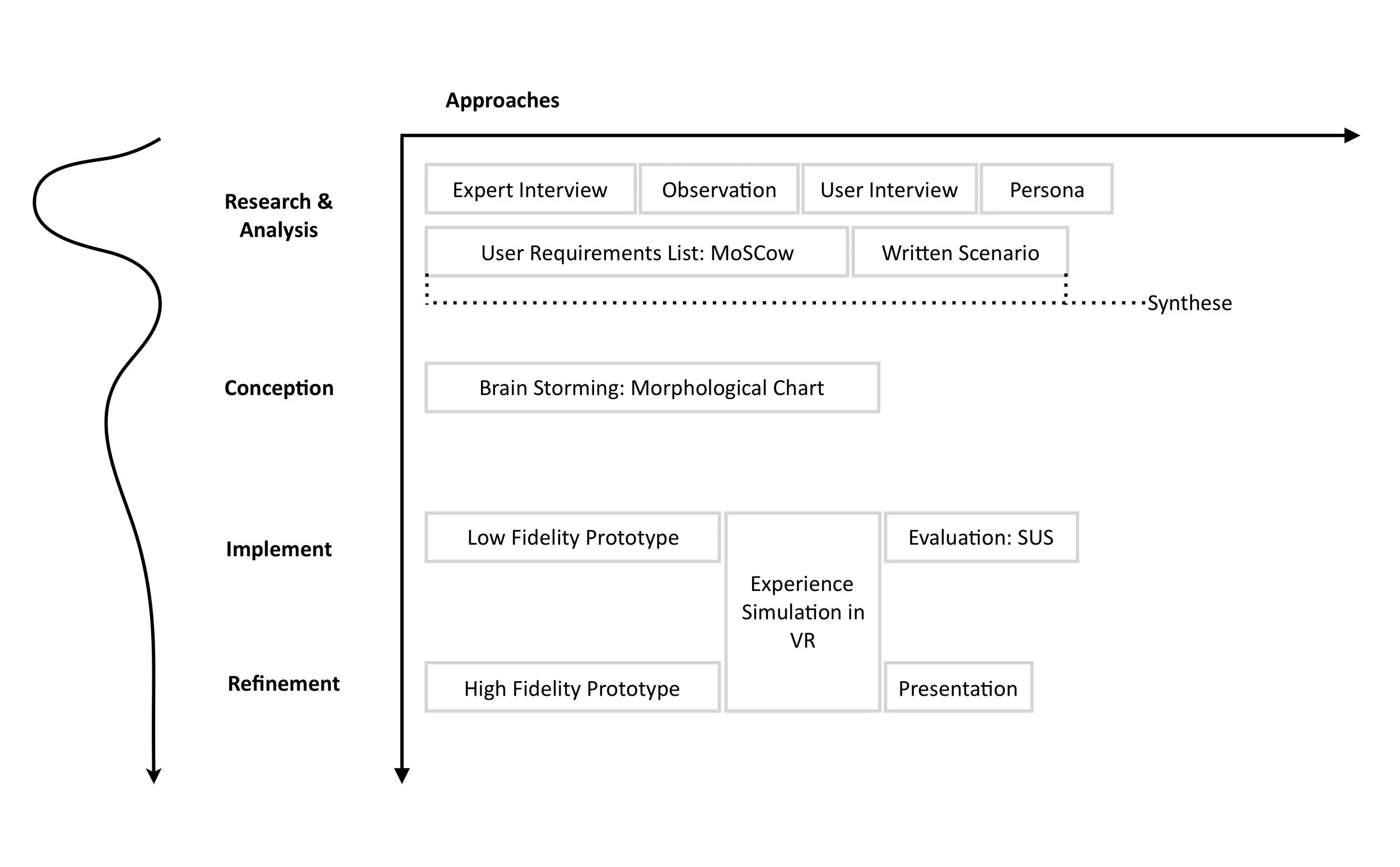
Overview of the Design Process
My Focus
An appropriately functioning solution to the problem
To attain such a solution, I have tried to find out the real reasons behind the low societal acceptance of autonomous vehicles. Proposals for the problem were developed through a participatory design process and were carefully tested by the users themselves.
Research & Analyse Phase
Secondary research, Experts Interviews, Field study, User Interview, Persona
Field Study
Background Knowledge
Since the project involves different kinds of professional background knowledge, I conducted comprehensive secondary research including reviews of surveys, literatures, executed experiments and bench marks in relevant topics. In addition, I conducted 5 expert interviews with experts from engineering, design and psychology fields.
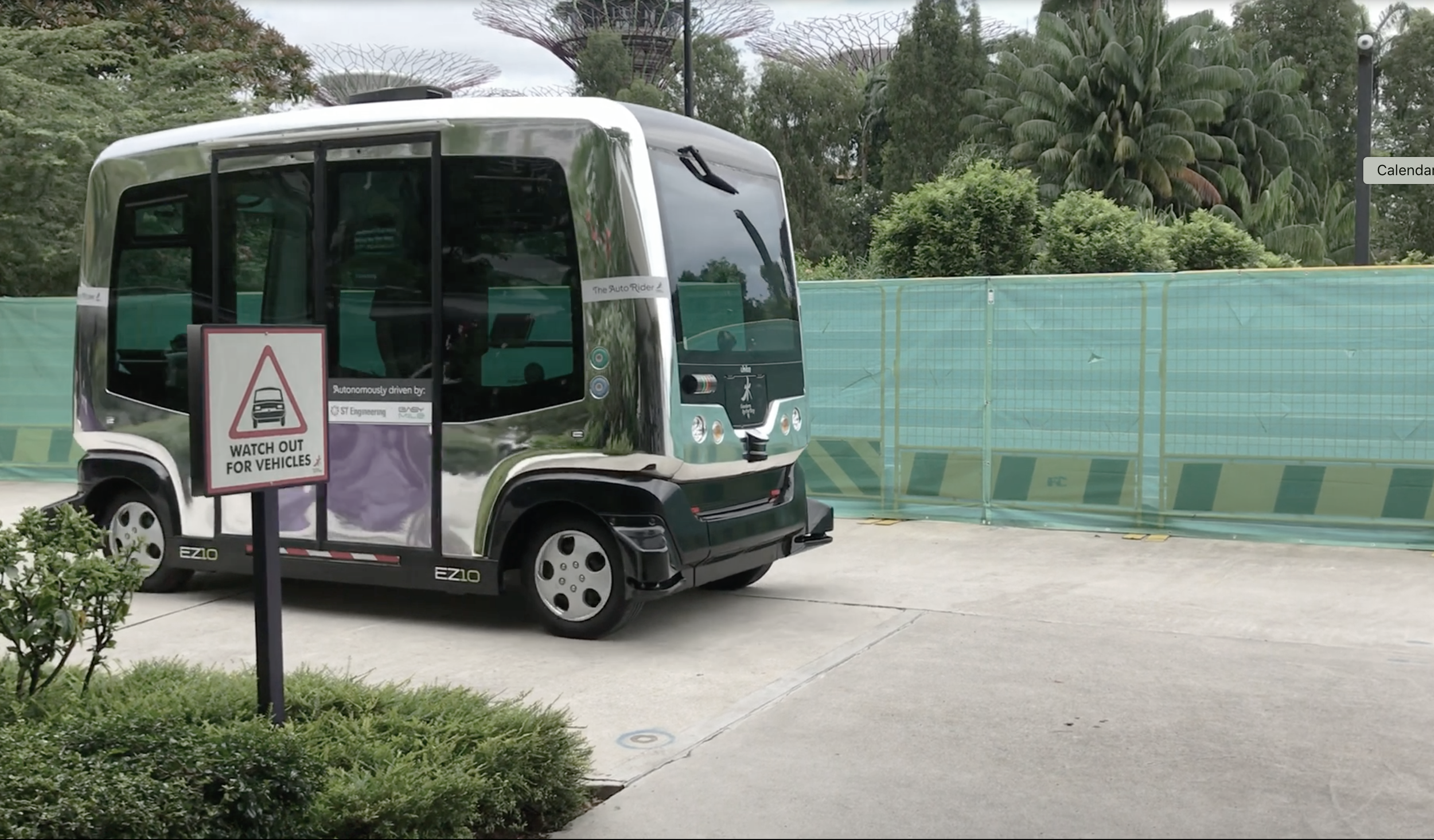
After gaining an overview of the problem context, I observed Singaporean bus transport and the operation of its fully autonomous bus AutoRider in Garden by the Bay. Meanwhile, I also tried the method Bodystorming on the Singaporean bus.
Uses‘ Insight
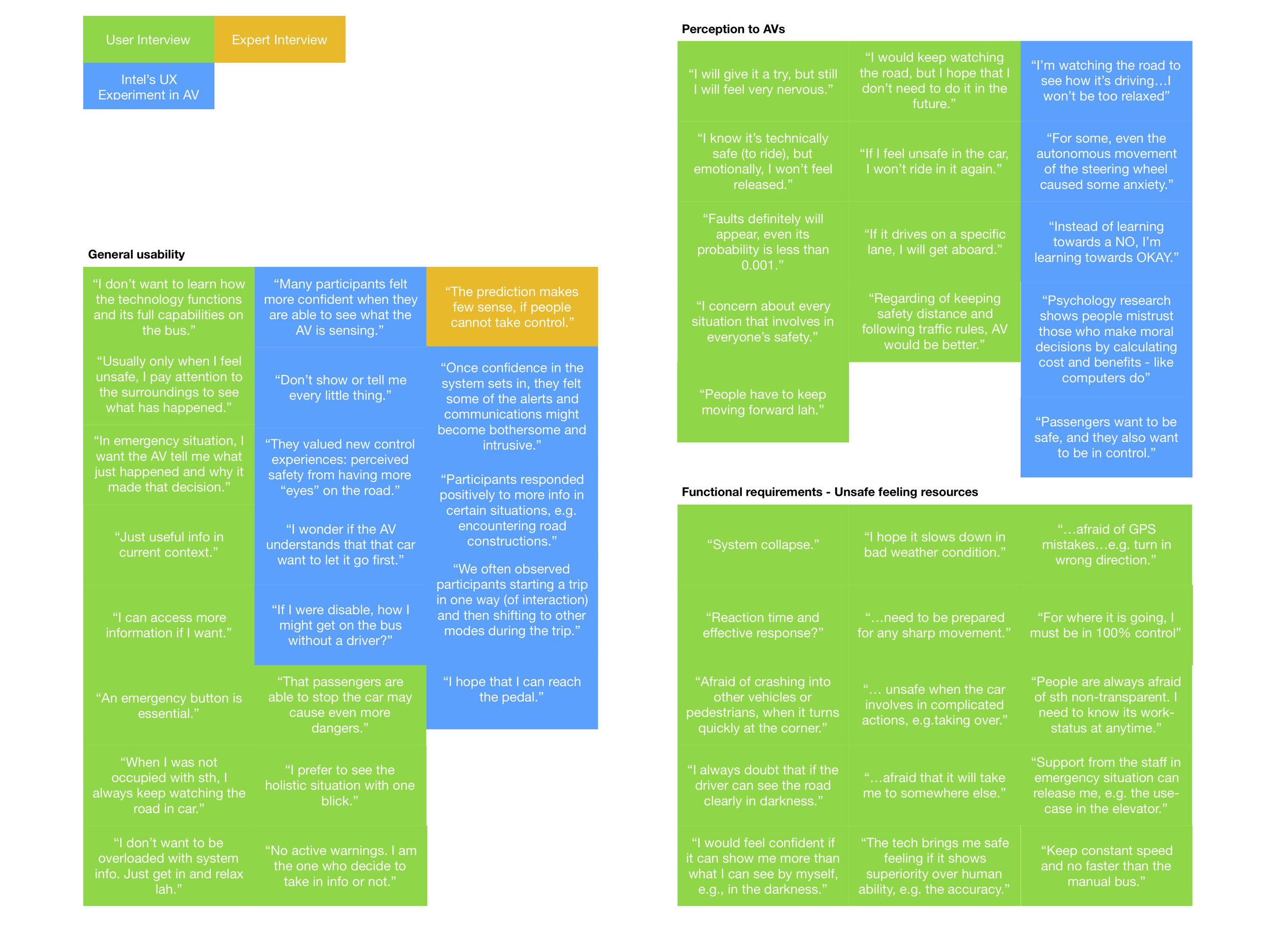
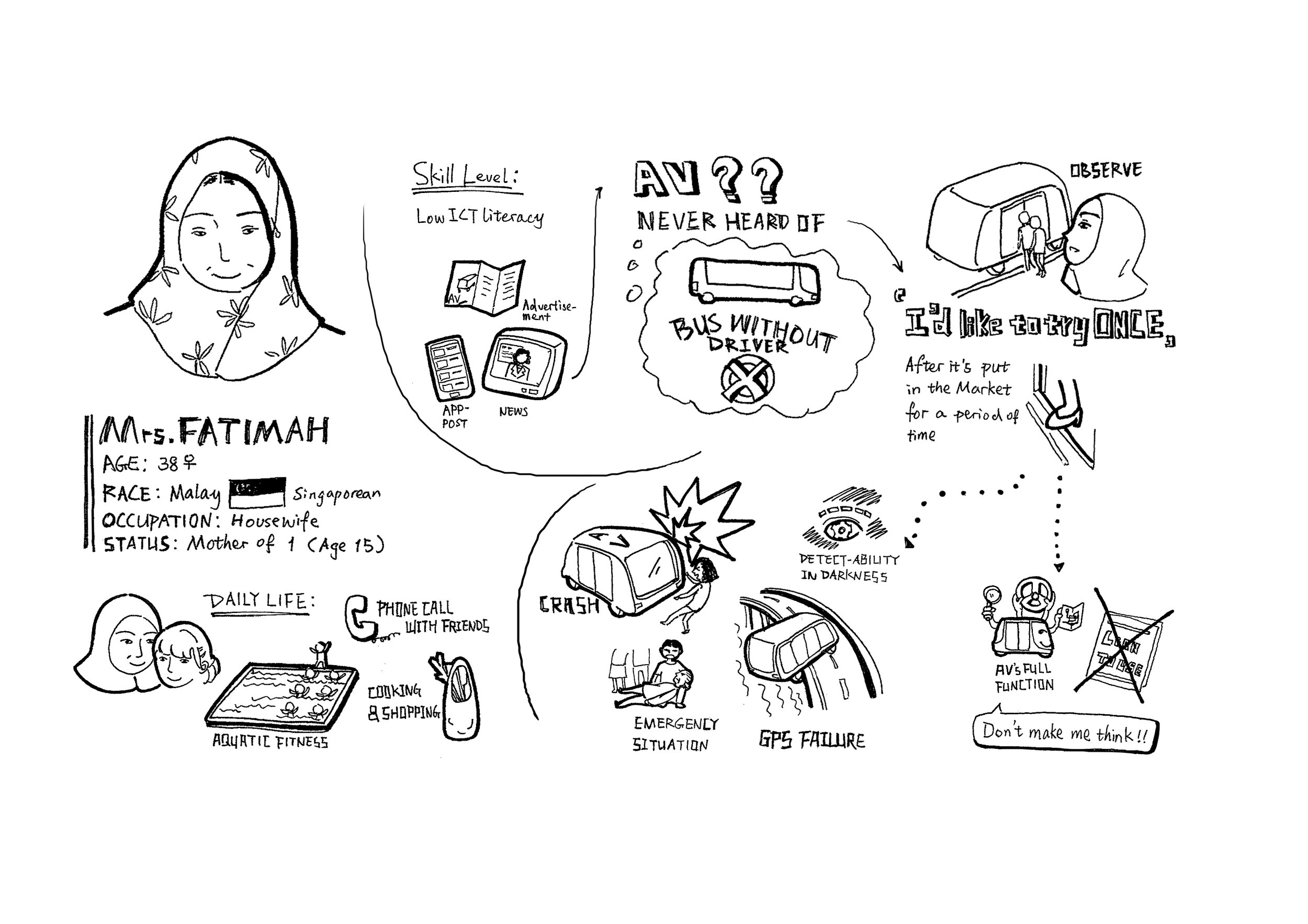
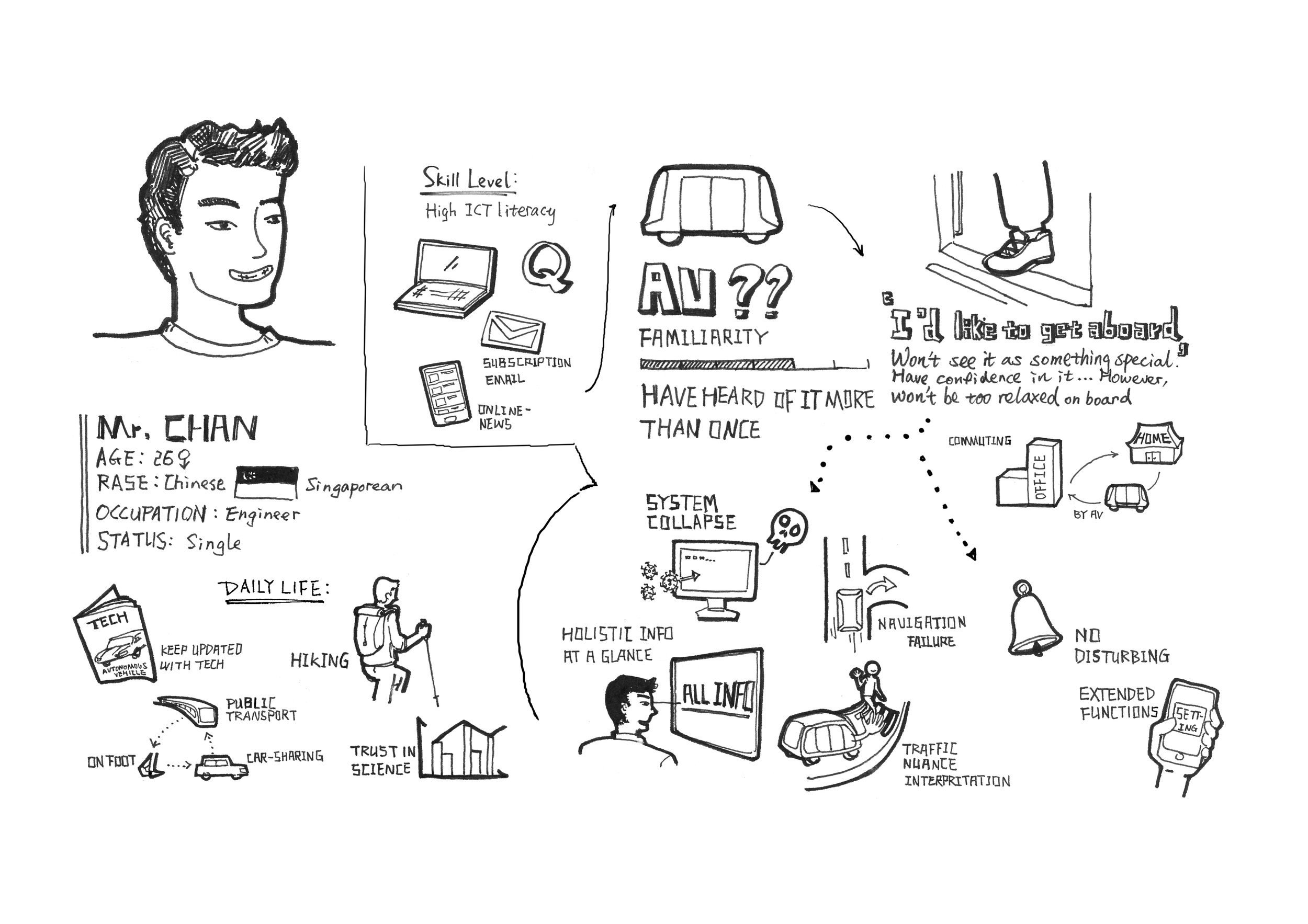
In order to gathering more insights to the user’s perception of the problem, 10 user interviews were conducted in downtown in Singapore. Combined with the collected data from expert interviews and the user research from Intel, a chart with selected remarks was formed to represent the perception and requirements from my users. 2 personas were created to conclude my understanding of my user, which were used as one of the criteria to check design decisions in later phases.
Synthesis
Insight, User Requirements List
Insight
A design solution that can help passengers better understand the intention and behaviour of the autonomous bus should be developed to ease their anxiety.
User Requirements List
I clarified the collected user requirements with a prioritisation technique called “MoSCow”. The highlighted user requirements are listed as below:

Conception
Concept Exploration, Concept selection
Concept Exploration
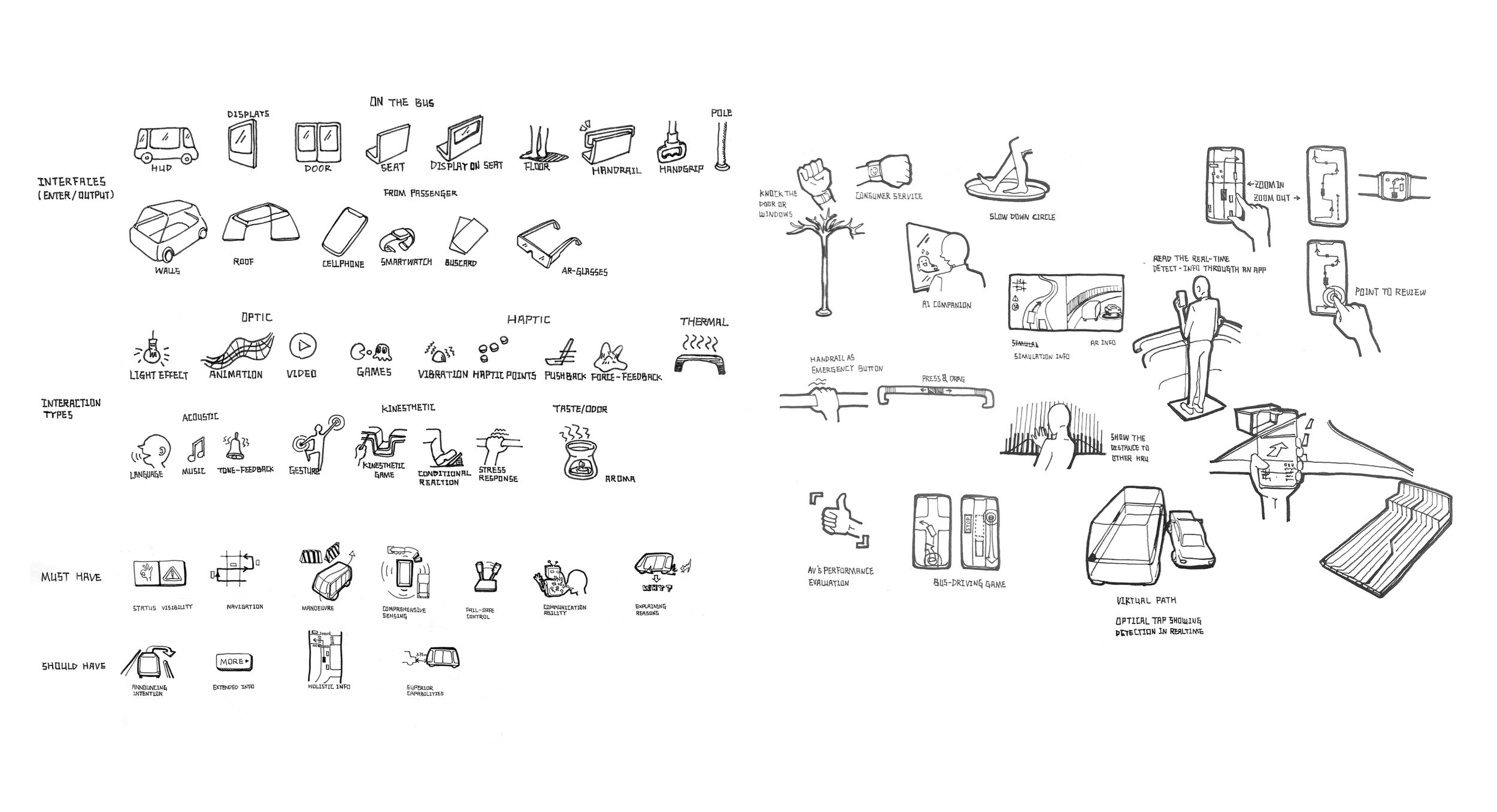
I broadened my ideation with the help of a morphological chart. All possibilities for the interface and interaction types, as well as the “Must have” and “Could have” functions are listed in the diagram. I selected items from its sublists and combined them to generate new concepts. From these, four ideas were chosen and further developed.
Concept Selection
With the help of an expert interview with a psychologist, my personas and my requirement catalogue, I finally narrowed down the 4 design directions to the one that shows what the bus has perceived. Based on the design direction, 5 different variants were developed to determine the best way for communicating the machine’s perception and intention:
1. Light Indications:
2. Sharing the Computer Vision with bus passengers:

e. A combination of “b” (the augmented view) and c (the abstract view).
Implementation
Prototyping, User Test
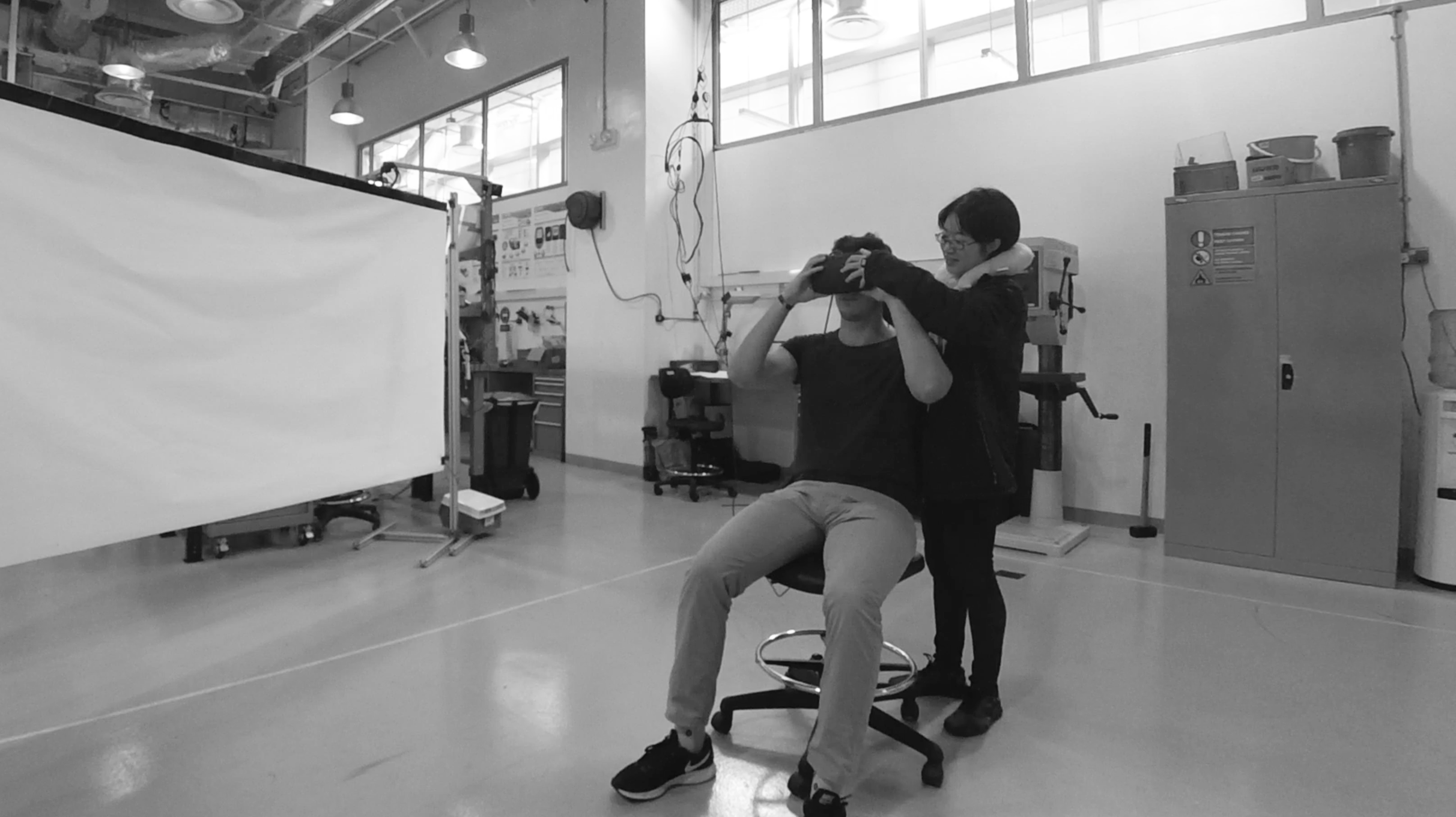
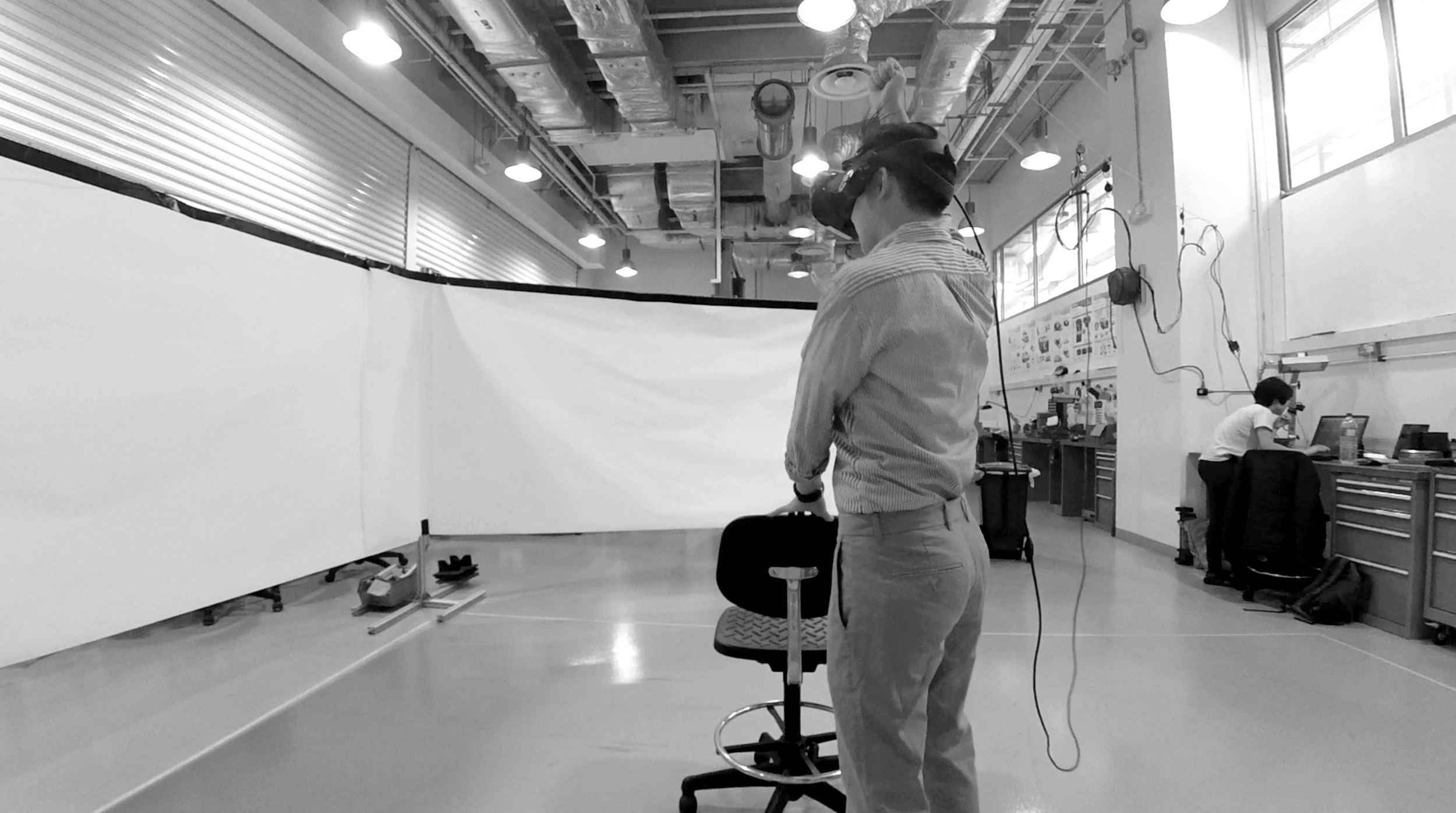
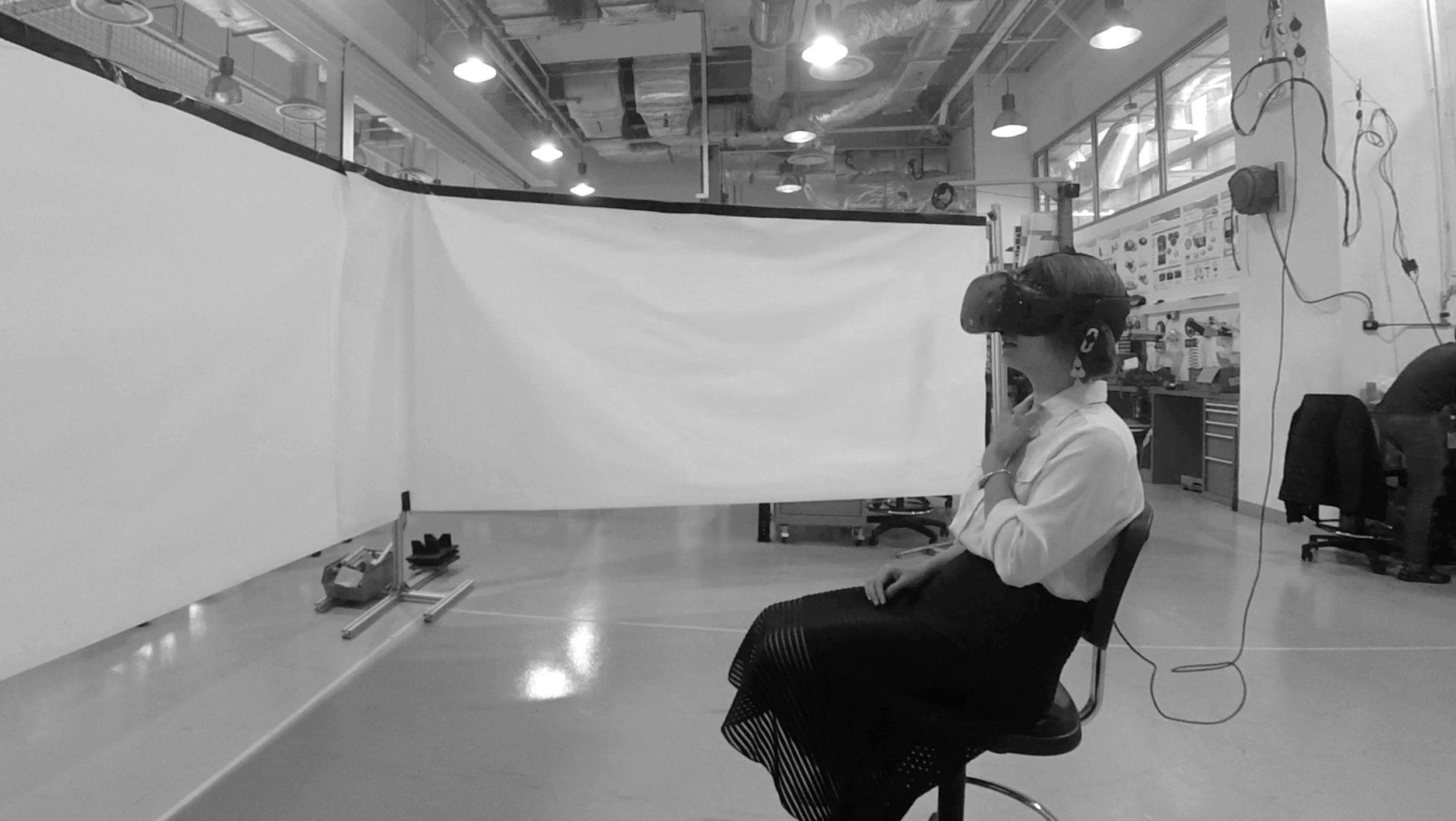
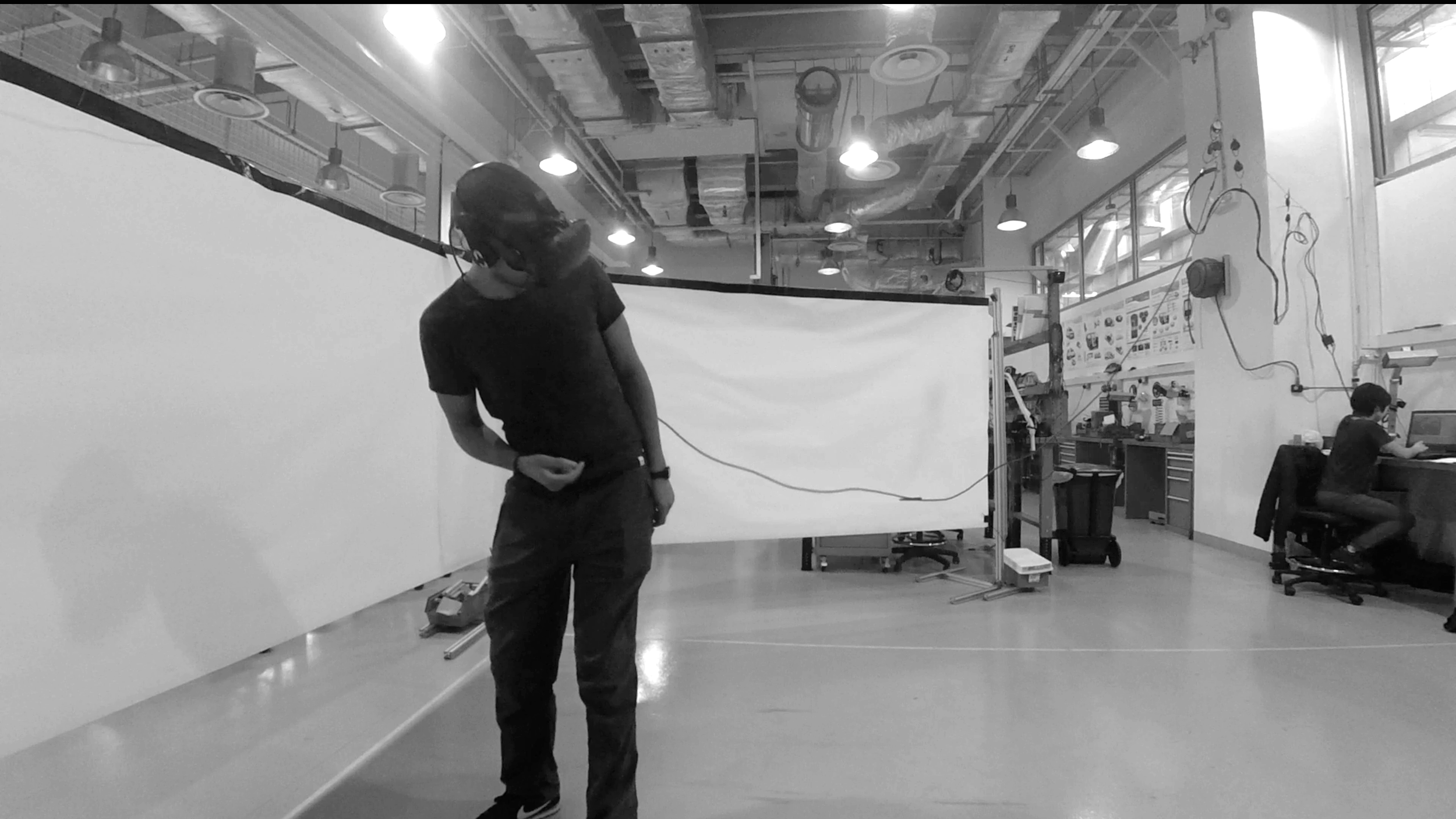
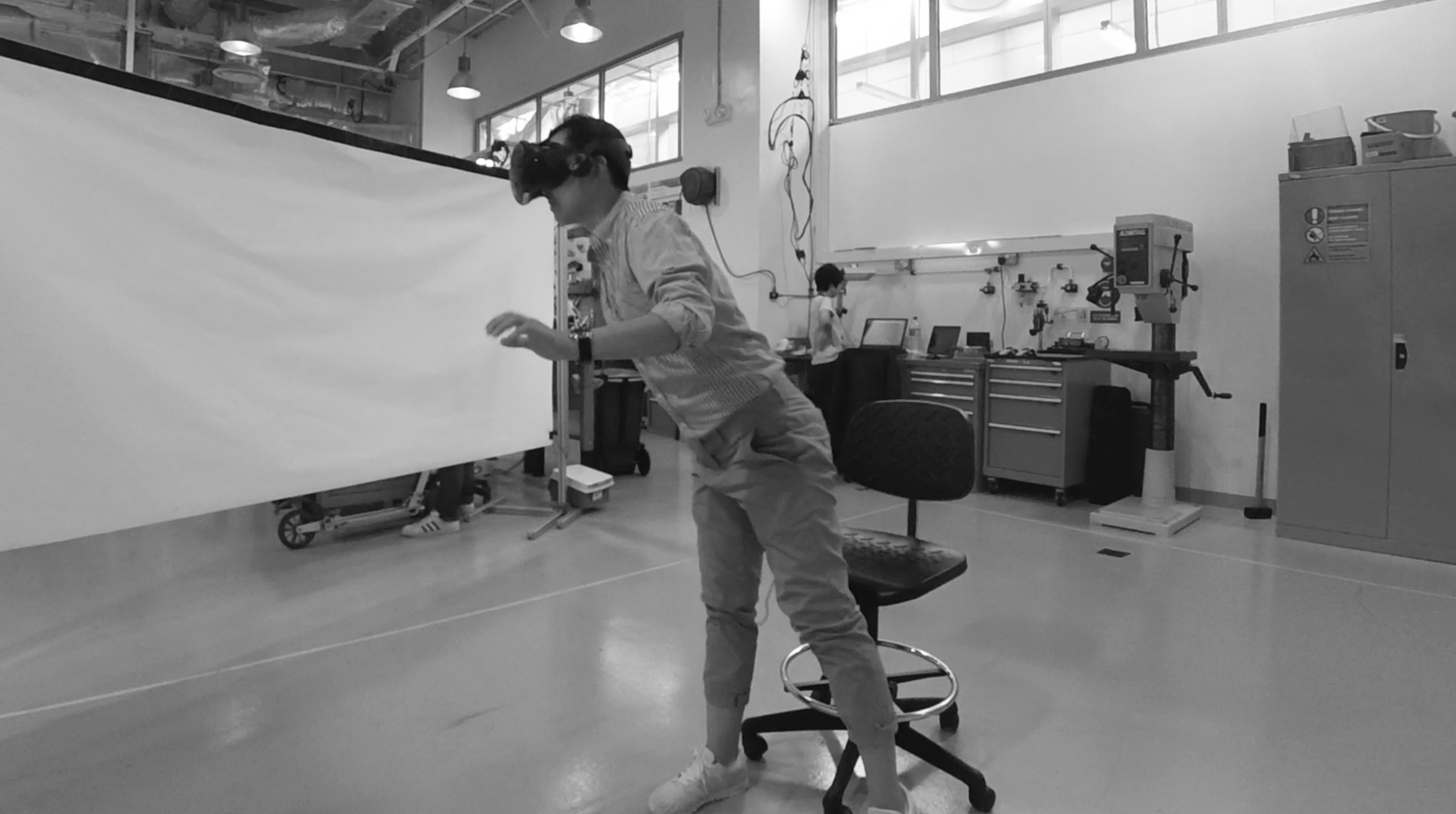
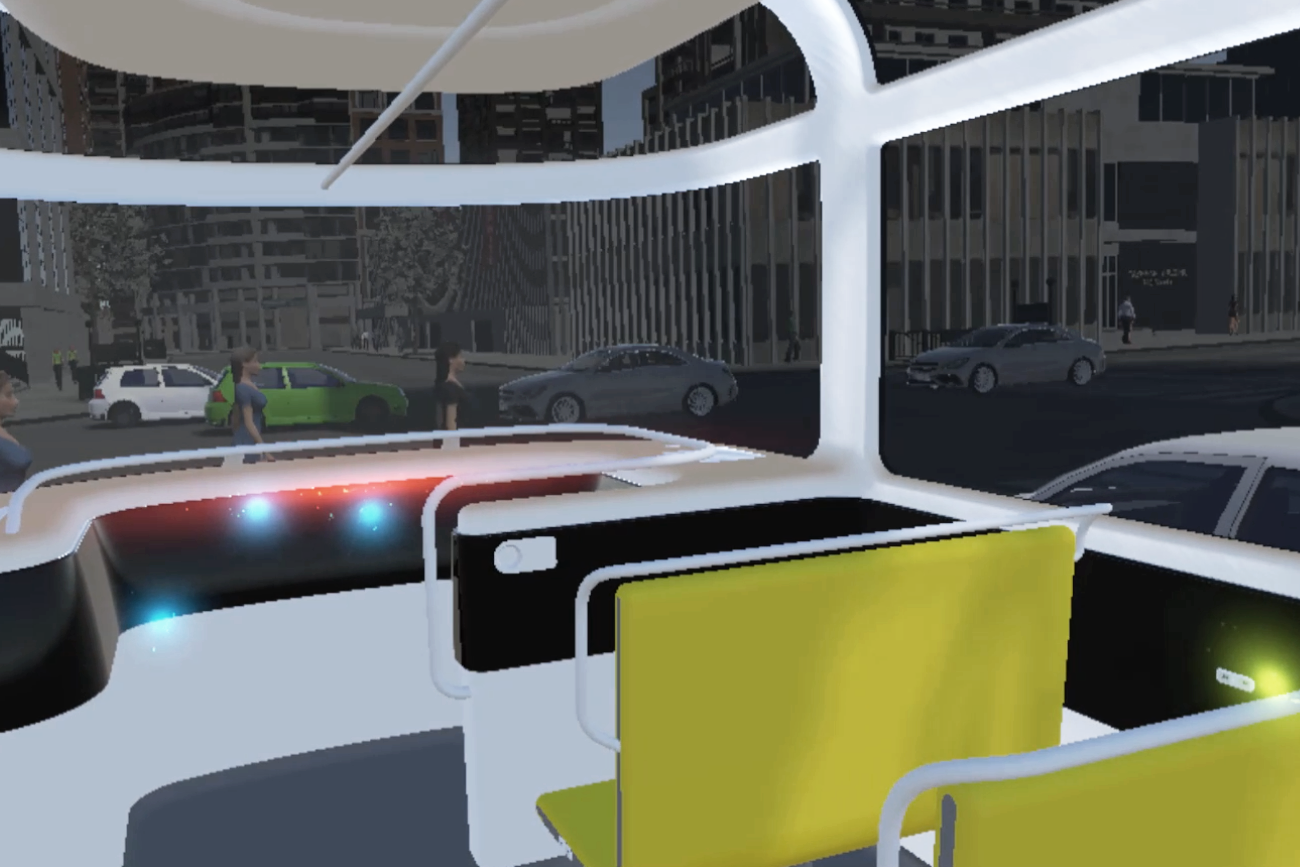
Prototyping - Experience Simulation by Using Virtual Reality (VR)
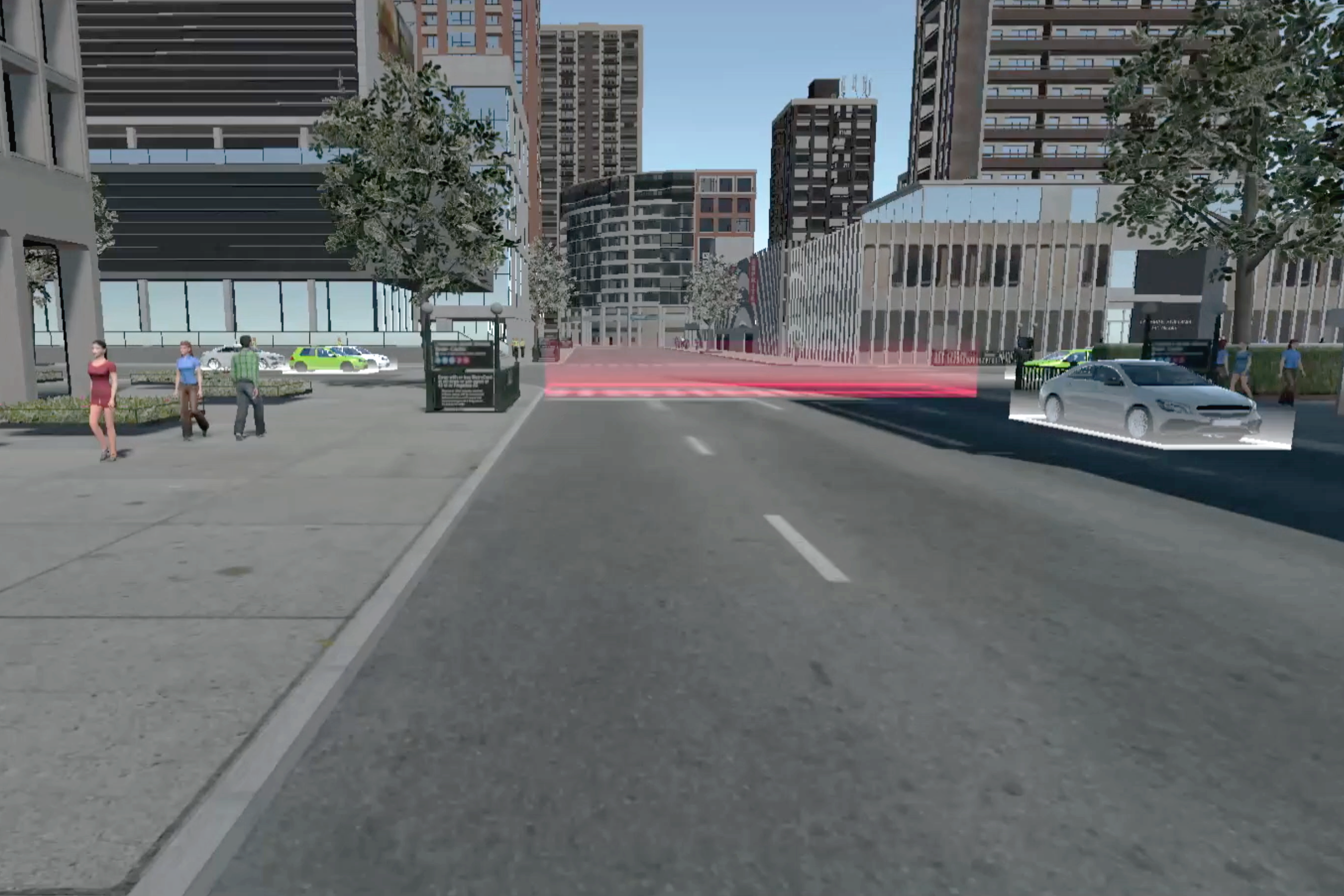
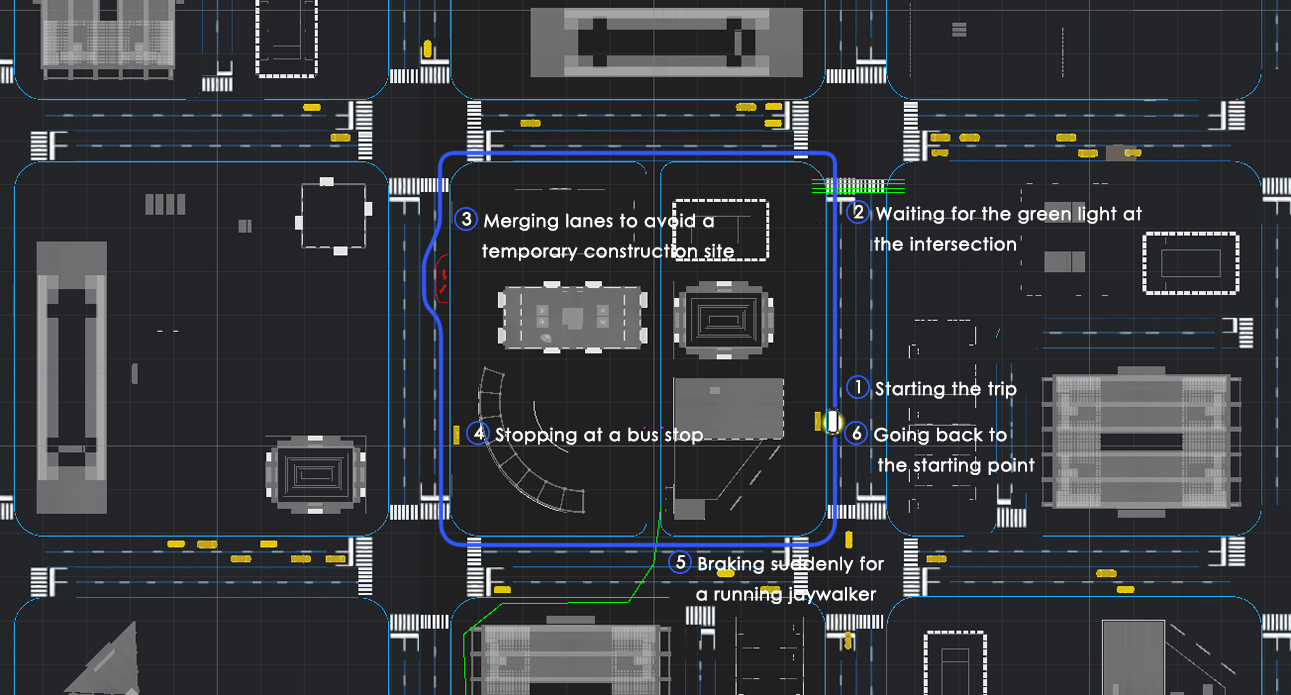
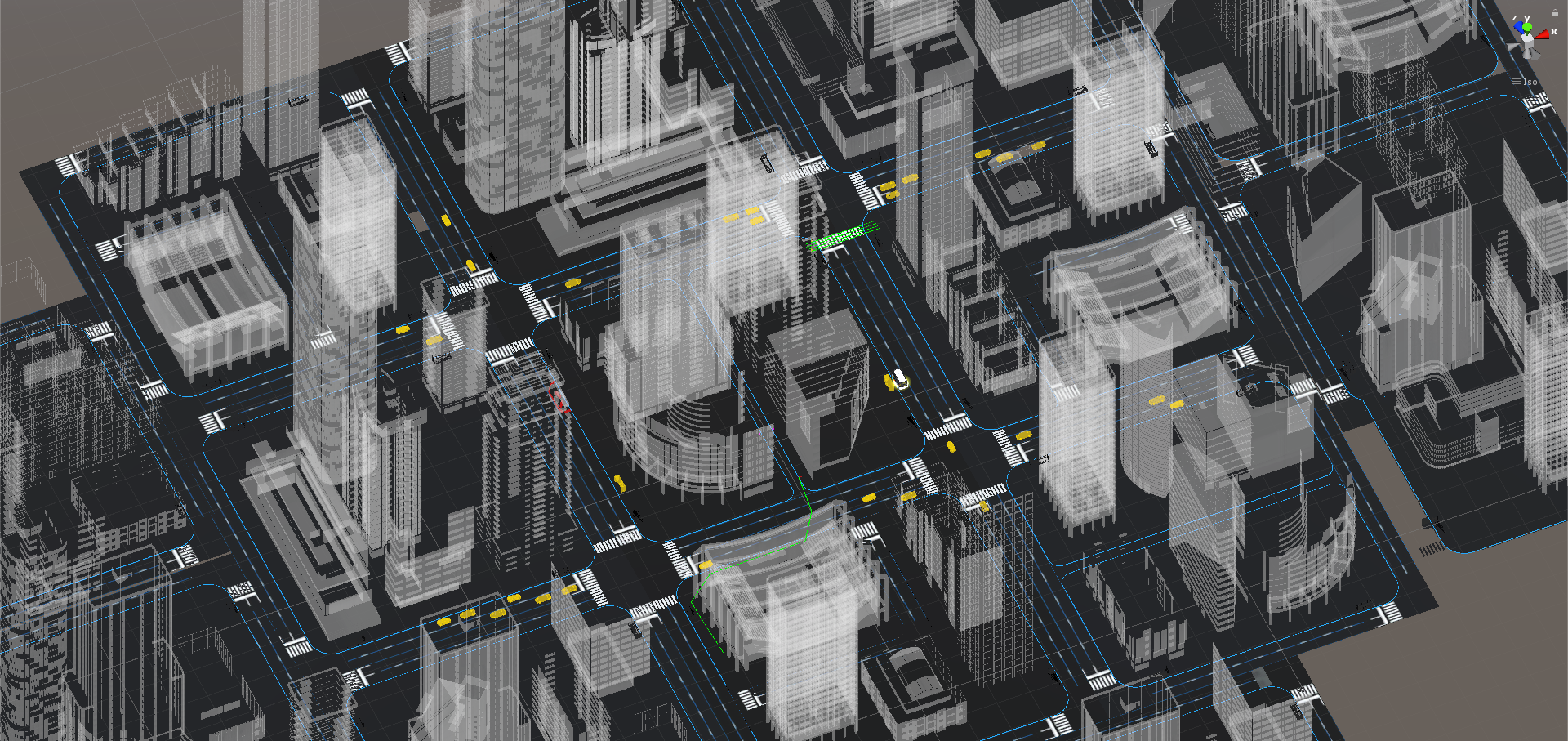
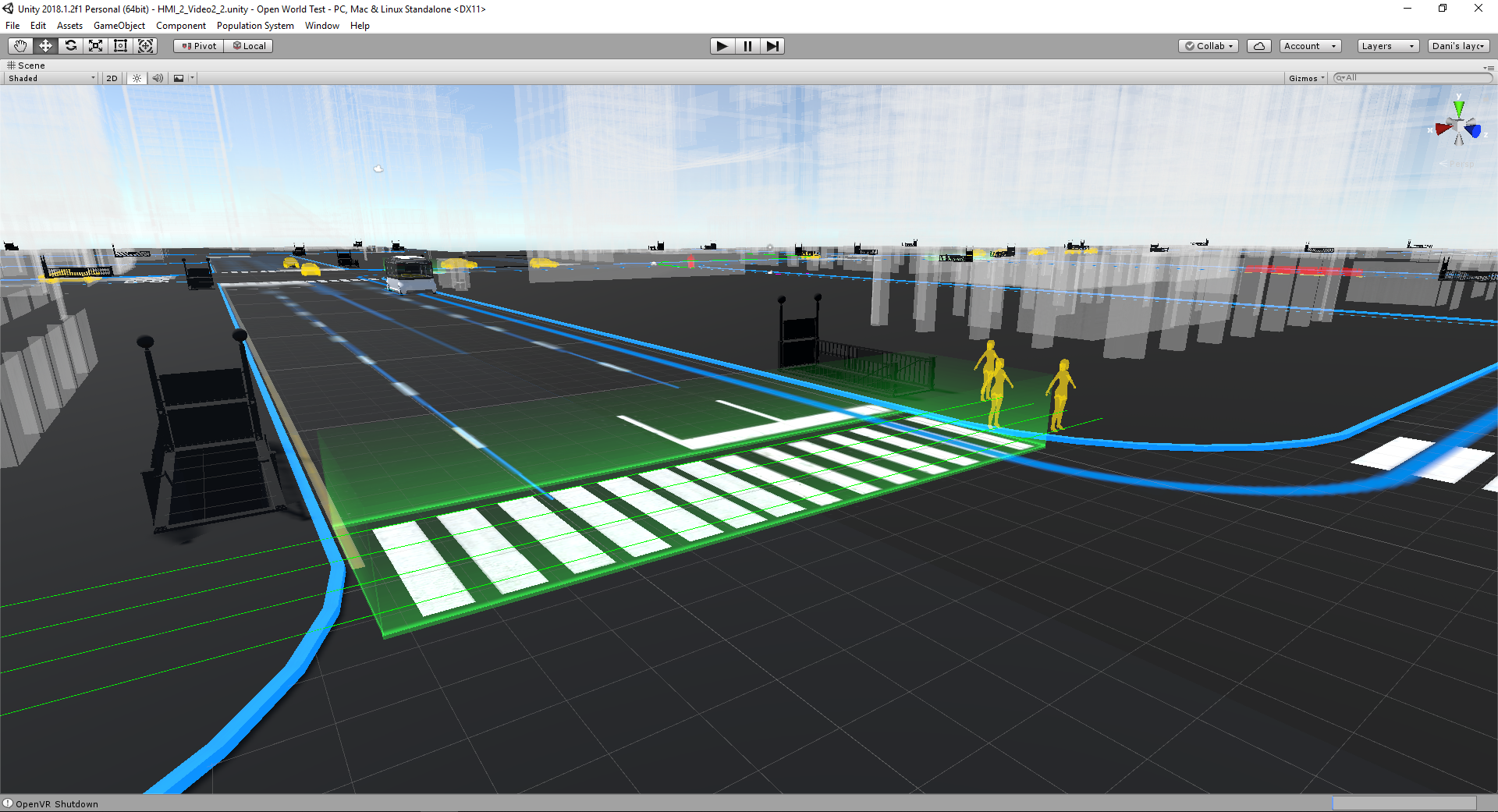
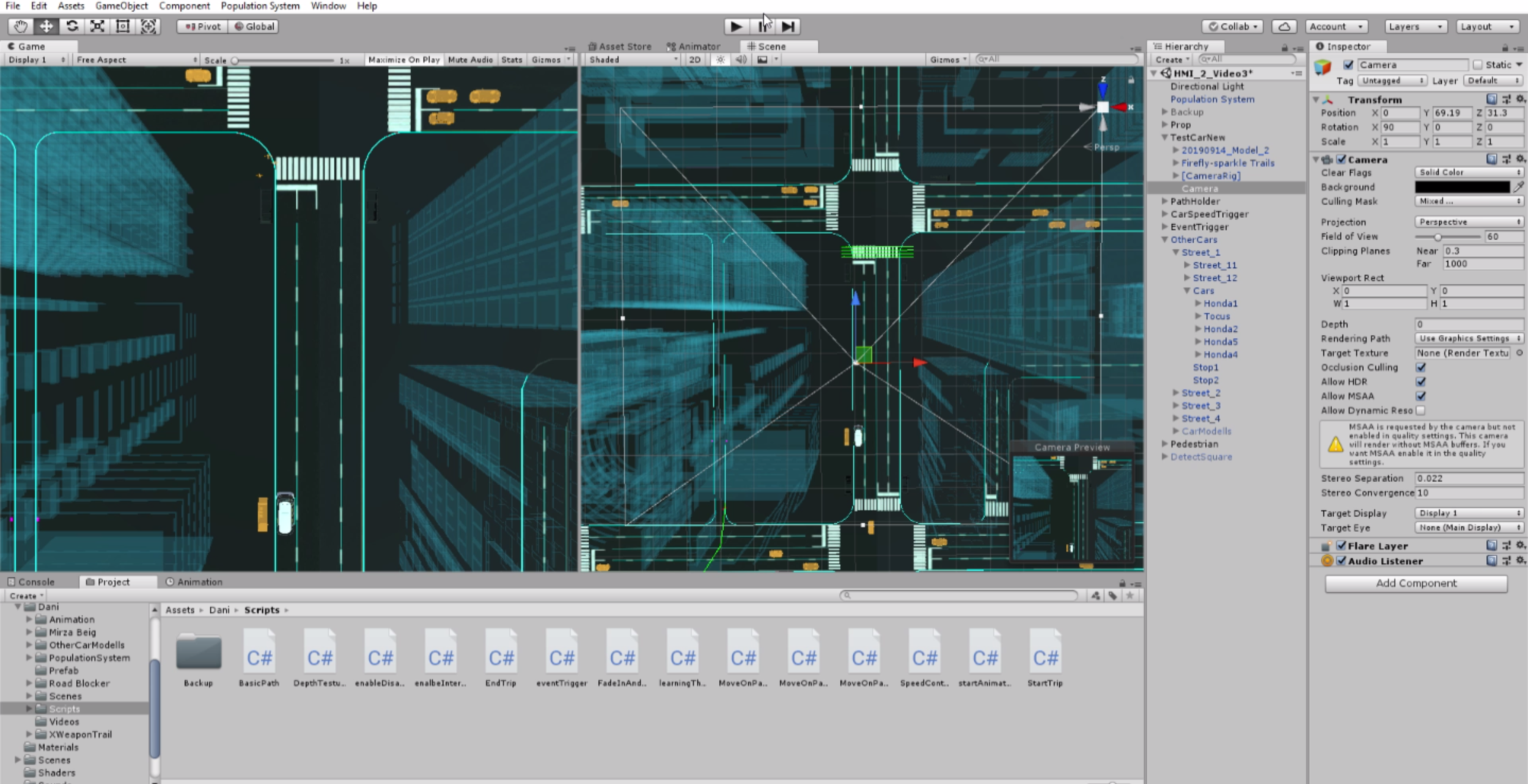
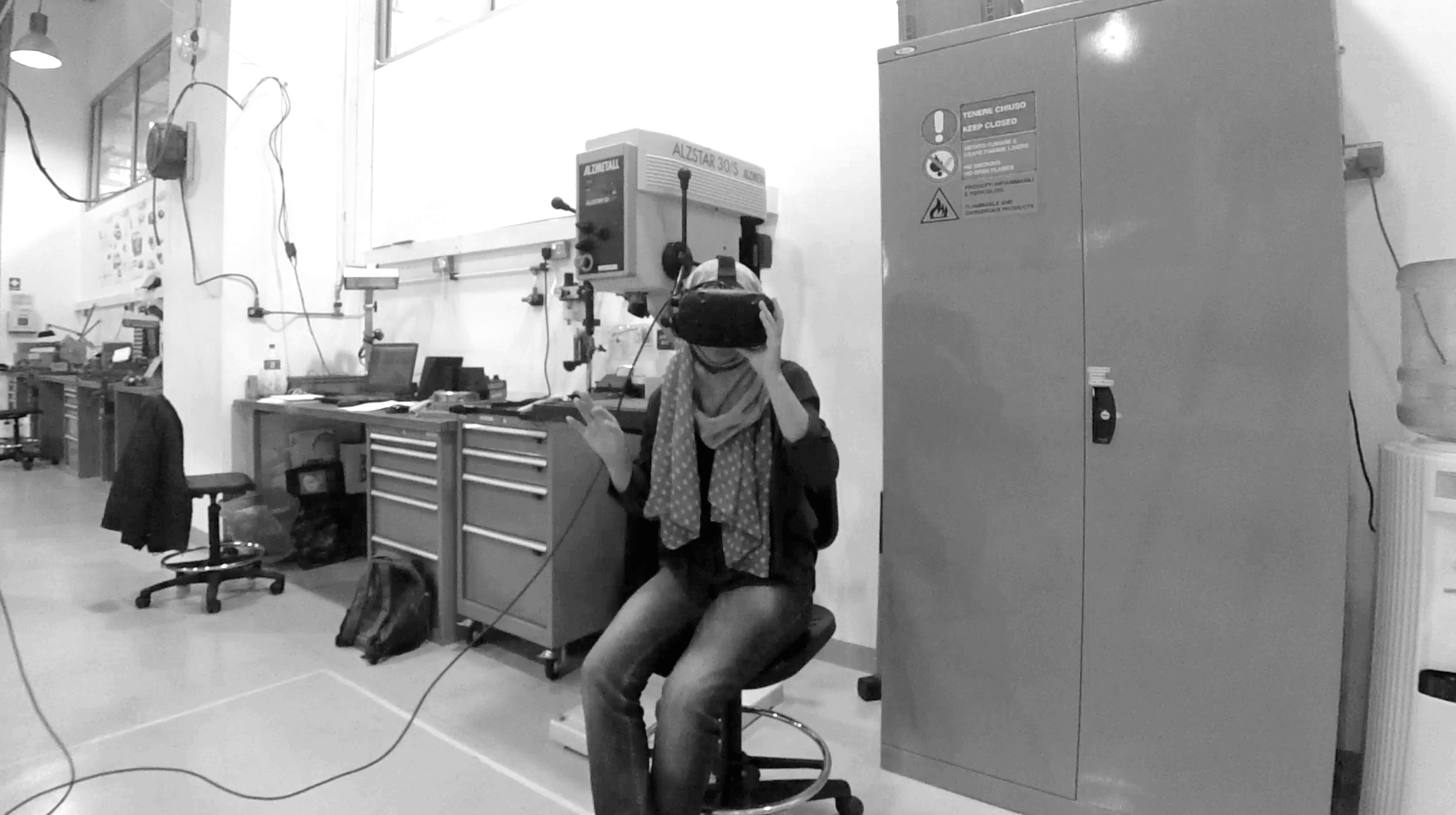
In order to develop a functioning system with the most suitability, I used the Experience Simulation method. The method focuses on the interaction behaviour, which occurs while engaging in new services. It requires user observation in an “ideal” using context. Instead of reconstructing the real-world, which is almost unfeasible, very time- and cost-consuming and might cause serious safety issues, a useful low cost alternative, the VR technique, was used to apply the Experience Simulation method. With the help of VR, the user and I were able to immerse into the environment and experience the design under various conditions. Therefore, all of the interactions were implemented and tested in Unity with VR. A virtual city with walking pedestrians, traffic and infrastructure, as well as a series of typical traffic events were also created in the scene.
The User Test
Seven users were invited to take part in the experiment with six virtual trial rides wearing the HTC Vive VR glasses. The trails consist of one control group without any HMI and the other five with different concepts.
User observation, questionnaires and user interviews were conducted in the experiment to collect useful data for user experience evaluation. For the questionnaire, I used a 5-points Likert scale, which was developed based on the System Usability Scale. Average usability scores were calculated according to the questions to ascertain the subjective feedback from the users.
Insight
The Effectiveness of the Solution
The Validity of the Data
User Feedback
Most of the participants share the common belief that the virtual scene is engaging and convincing. That belief means the result of that specific test is valid and is capable of indicating which of the requirements should be refined in the post-development phase.
Participants mentioned that they felt uncertain and unsafe during the simulation. In comparison with the control group (without HMI), the trials with HMI designs made the participants feel more relaxed. Therefore, the solution of using HMI to increase communication transparency between the passengers and the machine mind is effective at reducing the passengers’ anxiety.
According to the average usability scores from the questionnaires, the design direction of displaying the computer vision on the screen was preferred compared to using light indications. Moreover, the 3rd-person-view content display was the favourite.
Refinement
I was able to refine my requirements list by implementing feedback from the users. Some functions were added, such as an overview of the route and problems, such as the unergonomic position of the display, were fixed in the refinement phase. The final concept was tested and presented in VR.